Deep-Sea Octopuses: Exploring the Abyss
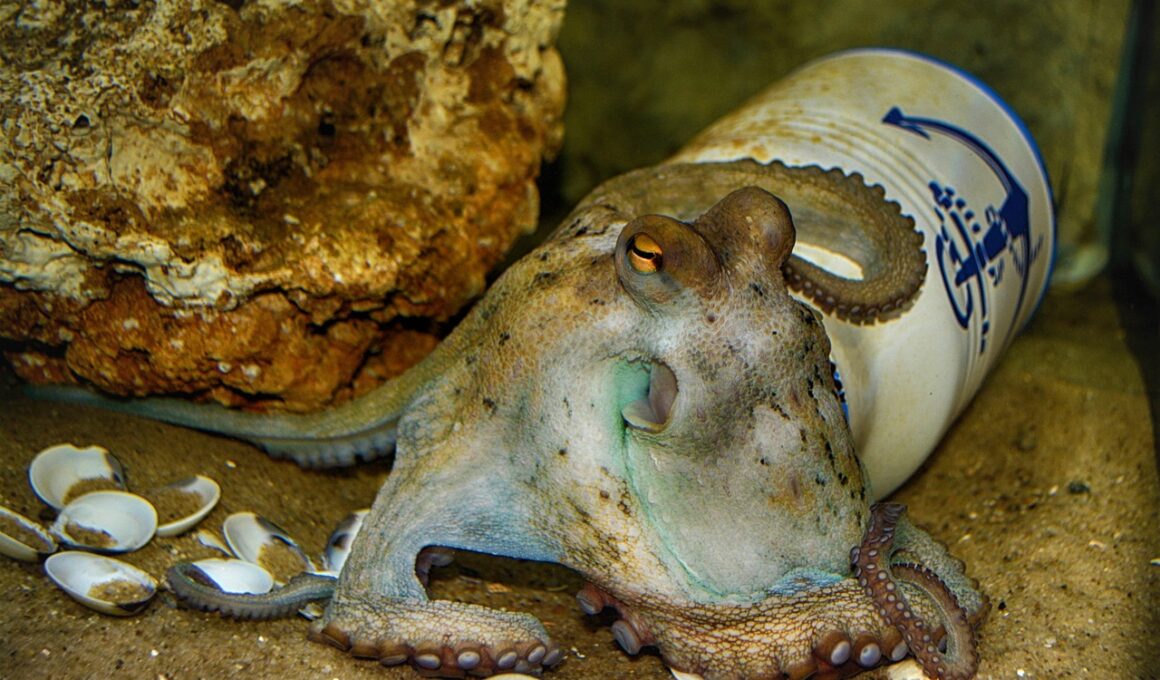
Deep-sea octopuses are fascinating creatures that inhabit the mysterious depths of our oceans. These incredible marine animals are known for their complex behaviors and unique adaptations to extreme environments. Found at depths ranging from 200 meters to over 5,000 meters, these octopuses have evolved to thrive in darkness and high-pressure conditions. They possess specialized anatomical features, including bioluminescent abilities and advanced camouflage techniques that help them evade predators. Unlike their shallow-water relatives, deep-sea octopuses often exhibit slower metabolism and longer lifespans, which can reach several years. Their diet mainly consists of crustaceans, fish, and other small, unsuspecting organisms that they capture using their highly adaptive arms. Additionally, the octopuses possess an extraordinary ability to regenerate lost limbs, allowing them to survive encounters with predators effectively. Despite residing in one of the most remote environments on the planet, these creatures have become an essential part of deep-sea ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling and overall biodiversity. Moreover, researchers are continuously studying these organisms to gain insights into their behaviors and evolutionary history. Understanding deep-sea octopuses can help us better appreciate the complexity of ocean life.
Research into the biology of deep-sea octopuses reveals much about their adaptations to extreme conditions. These more obscure species, such as the Dumbo octopus and the Blanket octopus, showcase incredible morphological differences tailored for life in the deep. Deep-sea octopuses have developed specialized limbs that are not only highly flexible but also equipped with suckers to capture prey. Their unique pigmentation allows them to change colors rapidly, providing them with effective camouflage against predators. Moreover, one key adaptation is their ability to produce bioactive chemicals for defense. Some species have even been observed employing ink as a defense mechanism, similar to their shallow-water relatives. This ink serves to confuse predators and provide an opportunity for escape. Interestingly, deep-sea octopuses have also been studied for their reproductive habits, which differ significantly from their shallow-water counterparts. They typically exhibit a high degree of parental care, often guarding their eggs until they hatch. Furthermore, deep-sea octopus populations are generally less understood due to the difficulty of observing them in their natural habitats, highlighting the importance of continued exploration and research in these fascinating ecosystems.
Ecological Importance of Deep-Sea Octopuses
Deep-sea octopuses play a critical role in their ecosystems, acting as both predators and prey within the underwater food web. Their diet primarily consists of fish, crustaceans, and various invertebrates, effectively regulating these populations and contributing to the balance of marine life. By preying on smaller animals, they help control species that may otherwise overpopulate, assisting in maintaining biodiversity in the deep-sea environment. Additionally, octopuses themselves are also preyed upon by larger marine animals, such as sharks and larger fish species. This dual role exemplifies their importance in nutrient cycling and energy transfer within the marine ecosystem. Furthermore, the unique behaviors displayed by deep-sea octopuses can inspire biomimicry in technology and design. For example, their remarkable ability to camouflage could lead to advancements in materials and fabrics that change color or pattern based on surrounding environments. Studying deep-sea octopuses, and understanding their ecological significance, can inform conservation efforts and guide policymakers in protecting fragile marine ecosystems, particularly as the impacts of climate change challenge the health of ocean environments. Research dedicated to their preservation could unveil more mysteries hidden in the deep sea.
One of the most challenging aspects of studying deep-sea octopuses is their elusive nature and the remote environment they inhabit. Research expeditions often rely on advanced submersible technology and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) to explore these deep habitats. As a result, very few individuals have witnessed these creatures in their natural habitats. The limited access to these environments poses significant challenges for marine biologists and researchers looking to study their behaviors and ecological roles. Moreover, the data collected from such explorations often yield only glimpses into the lives of these fascinating octopuses. In many cases, researchers also encounter obstacles relating to the preservation of specimens and the ethical considerations surrounding their collection. In addition, the threats posed by deep-sea mining, pollution, and climate change are areas of growing concern. These human activities can disrupt the delicate ecosystems where deep-sea octopuses thrive, and potentially lead to population declines. This highlights an urgent need for increased awareness and protective legislation aimed at safeguarding the future of these remarkable oxygen breathers and their habitats, ensuring they continue to flourish in the depths of our oceans.
Conservation Challenges Facing Deep-Sea Octopuses
The conservation of deep-sea octopuses faces numerous challenges due to the ongoing degradation of marine habitats and the lack of comprehensive legal protection. The deep sea remains largely unexplored and poorly understood, resulting in regulatory frameworks that inadequately address the conservation needs of these species. Furthermore, as technology advances and deep-sea mining becomes more prevalent, the potential for habitat destruction increases, posing threats to the ecosystems these octopuses inhabit. Additionally, as global temperatures rise, changes in ocean chemistry, such as increased acidity and reduced oxygen levels, could have dire consequences on their populations and health. The impact of overfishing also affects their food sources, further complicating their survival. Consequently, it is critical to promote further research into the lives of deep-sea octopuses and their ecological roles, fostering an understanding that can inform conservation efforts. Educating the public about the importance of deep-sea ecosystems is crucial in driving support for legislative measures focused on habitat protection. By working collaboratively, scientists, conservationists, policymakers, and communities alike can take significant steps to ensure these incredible creatures and their habitats are preserved for future generations.
Many organizations and researchers are actively engaged in initiatives aimed at protecting deep-sea ecosystems and the fascinating creatures that inhabit them. Legislative efforts have been pursued globally to create marine protected areas (MPAs) that safeguard critical habitats from human exploitation. By establishing these zones, more efficient management and protection of vulnerable species, including deep-sea octopuses, can be achieved. Furthermore, international collaborations among scientists and conservationist organizations have been formed to gather more data about the habitats and behaviors of deep-sea marine species. The development of technology, such as underwater drones and autonomous underwater vehicles, enhances observation capabilities, enabling more thorough and regular surveys of the deep-sea environment. This technological advancement allows researchers to collect more comprehensive data, aiding in forming strategies to combat the threats faced by these marine animals. Engaging local communities and stakeholders is also vital for successful conservation efforts, fostering a sense of stewardship toward marine ecosystems. By collaborating with fishermen, scientists can develop sustainable fishing practices that help maintain balance in ocean biodiversity, showcasing a promising pathway toward sustainable coexistence with deep-sea octopuses and other marine life.
Future Directions for Research on Deep-Sea Octopuses
The future of research on deep-sea octopuses looks promising, as advancements in technology and increased funding for marine science initiatives pave the way for greater understanding of these elusive creatures. Continued exploration of the deep ocean will enable scientists to uncover new species and behaviors, shedding light on the evolutionary history and ecological significance of these fascinating animals. As our understanding of their habitats grows, researchers will be better equipped to assess the impacts of climate change and human activities on deep-sea ecosystems. Future studies may focus on behavioral ecology and reproductive strategies, yielding essential insights into their adaptations in deep, dark environments. Additionally, developing non-invasive monitoring techniques, such as environmental DNA sampling, can help detect deep-sea octopus populations without direct interaction, minimizing stress on the species. Enhanced collaborative efforts among international scientists will facilitate knowledge-sharing and joint research projects, leading to more comprehensive approaches to conservation. Finally, the integration of outreach and education initiatives will foster greater public interest and support for deep-sea exploration and conservation, ensuring that future generations appreciate the wonders and importance of deep-sea octopuses within our oceans.
In conclusion, deep-sea octopuses represent some of the most remarkable and adaptable creatures in the ocean, showcasing extraordinary evolutionary traits suited to their unique deep-sea environments. The ecological role they play underscores the complexity and interconnectedness of marine life, highlighting the need for continued research and efficient conservation efforts. Understanding the behaviors, biology, and ecological importance of these creatures is crucial for preserving not only their populations but also the intricate ecosystems they inhabit. As we continue to explore the depths of our oceans, we unveil new mysteries that can enhance our appreciation for marine biodiversity. Together, scientists, conservationists, and the public must work towards sustainable practices that protect these incredible organisms. By supporting initiatives aimed at preserving deep-sea octopuses and their habitats, we can contribute to the health of our oceans and the planet as a whole. The journey to uncovering the secrets of deep-sea octopuses is just beginning, and with every exploration, we gain invaluable insights into the richness of marine life. Let us champion their conservation, ensuring future generations can experience the wonder of deep-sea octopuses and their underwater realms.