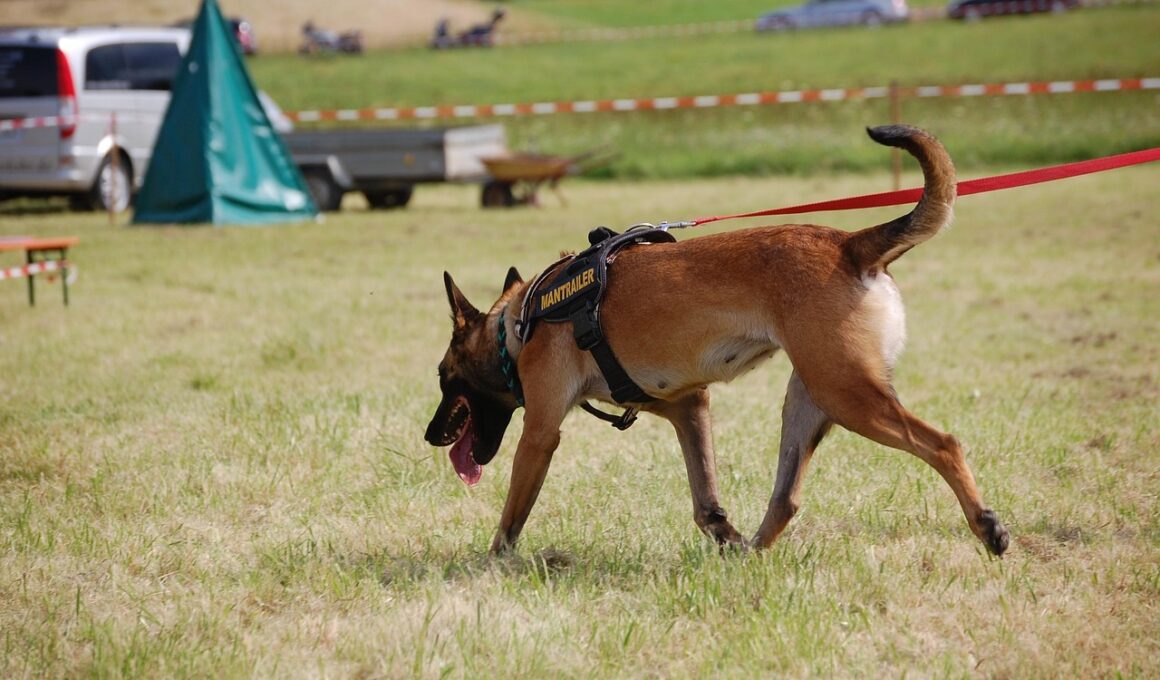
The Role of Scent Discrimination in Search and Rescue Work
Scent discrimination is an essential skill that search and rescue (SAR) dogs exhibit, allowing them to effectively distinguish between various scents in complex environments. Dogs possess a remarkable sense of smell, estimated to be between 10,000 to 100,000 times more sensitive than that of humans. This ability helps them locate missing persons in outdoor settings, disaster zones, and various terrains. SAR dogs utilize their noses to identify specific scents associated with a person, often including smells from the skin, clothing, and personal belongings. Their training involves exposing them to many scents so they learn to focus on the target scent amid numerous distractions. During real-life operations, a dog’s quick ability to filter scents speeds up locating individuals in distress. Handlers also benefit from their dogs’ skills, as they can interpret the dog’s behavior and alerts in the search process. The bond between the dog and handler significantly enhances efficiency. As a result, teams can navigate through potentially dangerous or overwhelming situations by relying on their dog’s refined sense of smell, demonstrating the critical role that scent discrimination plays in SAR scenarios.
Scent discrimination becomes particularly vital in urban disasters where scents can easily intermingle and confuse the dog’s tracking abilities. For example, in the aftermath of a collapsed building or a hazardous site, the distinct aromas of debris, smoke, and other environmental factors can mask the target scent. With rigorous training, SAR dogs learn to hone in on specific scents they associate with the individuals they have been trained to find. Handlers must ensure that these working dogs practice in various environments to prepare them for challenging situations. Utilizing scent training exercises in different locations smoothens their adaptation to new and confusing scenarios. SAR teams may employ methods like hiding scent samples in various areas while stimulating distractions to reinforce the dog’s focus on the task. Proper scent classification is essential; incorrectly identifying a unique scent leads to ineffective searches and wasted efforts. Continuous training helps to maintain their sensitivity and adaptability, allowing SAR dogs to improve their performance when locating missing persons. Ultimately, precise scent discrimination not only aids in successful missions but also ensures the safety of distressed individuals in crisis situations.
The Science Behind a Dog’s Sense of Smell
The canine olfactory system is a marvel of evolution, equipped with approximately 300 million olfactory receptors compared to the mere 5 million present in humans. This disparity contributes to dogs interpreting scents in ways humans cannot comprehend. These receptors create an intricate neural pathway to the brain, allowing dogs to discriminate and identify individual odors with remarkable accuracy. The structure of a dog’s nose includes turbinates and olfactory bulbs at the back of the nasal cavity, which amplify and enhance their sense of smell. This biological design enables dogs to not only detect specific scents but also differentiate them from an overwhelming array of other smells. Furthermore, a dog’s ability to analyze scent information is linked to their emotional memories; familiar scents can evoke specific responses or behaviors. As SAR training emphasizes scent discrimination, handlers become equipped with techniques to boost their dogs’ performance through scent games and complex tracking exercises. By enhancing their focus on target scents, SAR teams improve accuracy and efficiency in locating individuals in need of rescue, showcasing how scent discrimination is grounded in the remarkable science behind a dog’s olfactory capabilities.
Building a strong partnership between the handler and the SAR dog is crucial for effective search and rescue missions. Trust and communication allow the team to work seamlessly, ensuring the dog is confident in following the scent trail while the handler interprets the dog’s responses accurately. SAR dogs respond to various cues from their handlers, including voice commands, body language, and even the slightest shift in the environment. Developing this bond often begins early in the dog’s training at an appropriate emotional and mental level. Handlers must engage in regular training sessions with their dogs to strengthen their teamwork. The correlation between physical fitness and performance during SAR operations acts as a critical factor. As dogs excel in obedience and agility tasks, their scent trailing abilities enhance significantly. Moreover, handlers often learn to recognize subtle changes in their dog’s body language; these cues indicate when the dog has picked up a scent or is experiencing frustration. Ultimately, a solid bond ensures that the handler can maintain a calm demeanor, supporting both their dog and themselves through high-stress situations in real rescue operations.
Challenges Faced During Search and Rescue Missions
Search and rescue missions can present several challenges that test the limitations of both dogs and their handlers. One significant factor is environmental conditions, such as extreme weather or challenging terrains like mountains or dense forests. SAR dogs may struggle to navigate such terrains, making their scent tracking more difficult. Adverse weather, particularly heavy rain or snow, can wash away or obscure the scents that dogs need to follow, thereby complicating search efforts. Additionally, distractive noises or unfamiliar scents, such as nearby wildlife or urban disturbances, may divert the dog’s focus from locating the target scent. Training for these challenges involves creating simulated scenarios and such environments during practice sessions, allowing SAR dogs to become accustomed to distractions. Handlers prepare to be adaptable, employing alternative strategies to keep their dogs engaged when faced with setbacks. In these cases, effective teamwork is essential—an aware handler can observe their dog’s behavior and clue in on when to change direction or strategy during a search. A prepared SAR team can overcome these challenges and augment their chance of success under pressure.
In the context of search and rescue, the continual evaluation and analysis of dog performance play an essential role in overall mission success. Handlers need to assess not only their dog’s effectiveness in locating scents but also identify areas for improvement in their training and operational techniques. Regular evaluations can reveal changes in the dog’s abilities that arise due to age, health, or environmental factors. Additionally, implementing feedback from real missions helps fine-tune training parameters, adjusting approaches to maintain a high level of performance. Monitoring performance metrics, such as time taken to identify scents and the rate of success in locating missing persons, informs handlers of overall effectiveness. Veteran handlers often share their experiences with newer members during after-action reviews, fostering an environment of learning. SAR organizations may introduce various measures, including expert workshops or seminars, to further hone the skills of both the dogs and their handlers. Fostering adaptability within the SAR teams prepares them for unpredictable circumstances. Uniting knowledge, evaluation, and communication leads to continuous improvement, ultimately ensuring effective search and rescue outcomes across varying scenarios.
Conclusion: The Impact of Scent Discrimination
The value of scent discrimination in search and rescue operations cannot be overstated; it is the foundation upon which successful missions are built. The incredible abilities of SAR dogs to detect, analyze, and distinguish scents greatly enhance the chances of locating missing persons quickly and effectively. Through rigorous training and a strong relationship with their handlers, these dogs and their teams develop the skills necessary to operate under significant pressure in various environmental contexts. By mastering scent recognition, SAR dogs fulfill critical roles while reinforcing the importance of training, teamwork, and adaptability in high-stakes scenarios. The multifaceted nature of scent discrimination extends beyond mere skills; it embodies a collaboration based on trust, understanding, and a shared goal. Advanced techniques in training continue to evolve, contributing to the ever-growing effectiveness of scent-discriminating canines. As the teams embrace the changing dynamics of search and rescue missions, their collective efforts underscore the vital link between human and canine collaboration. Thus, organizations can maximize their success rates, ultimately leading to saving lives and providing vital assistance in times of need.
Each of these paragraphs illustrates the profound nature of scent discrimination in search and rescue work, signifying its significance in life-saving missions. Understanding the science, challenges, and strategies associated with SAR dogs reveals a world where teamwork and innate canine abilities unite. The ongoing dedication to training and improvement ensures that rescue teams are effectively equipped to face the complexities that arise in emergencies, further highlighting the indispensable nature of SAR dogs in society. The high caliber of scent discrimination can indeed be a pivotal factor in transforming tragic situations into hopeful outcomes. More communities are actively incorporating these canine assets into their emergency response strategies, thus improving readiness and resilience. It’s essential to recognize that the bond between a handler and dog goes beyond performance metrics; it embodies compassion and commitment to saving lives. Enhanced training methods tailored to dogs’ nuanced capabilities continue to be developed, actively reshaping the landscape of search and rescue operations. Ultimately, the unique relationship fosters a culture of impact and significance, as team members strive toward ensuring a future where every rescue mission maximizes its efforts and effectiveness.