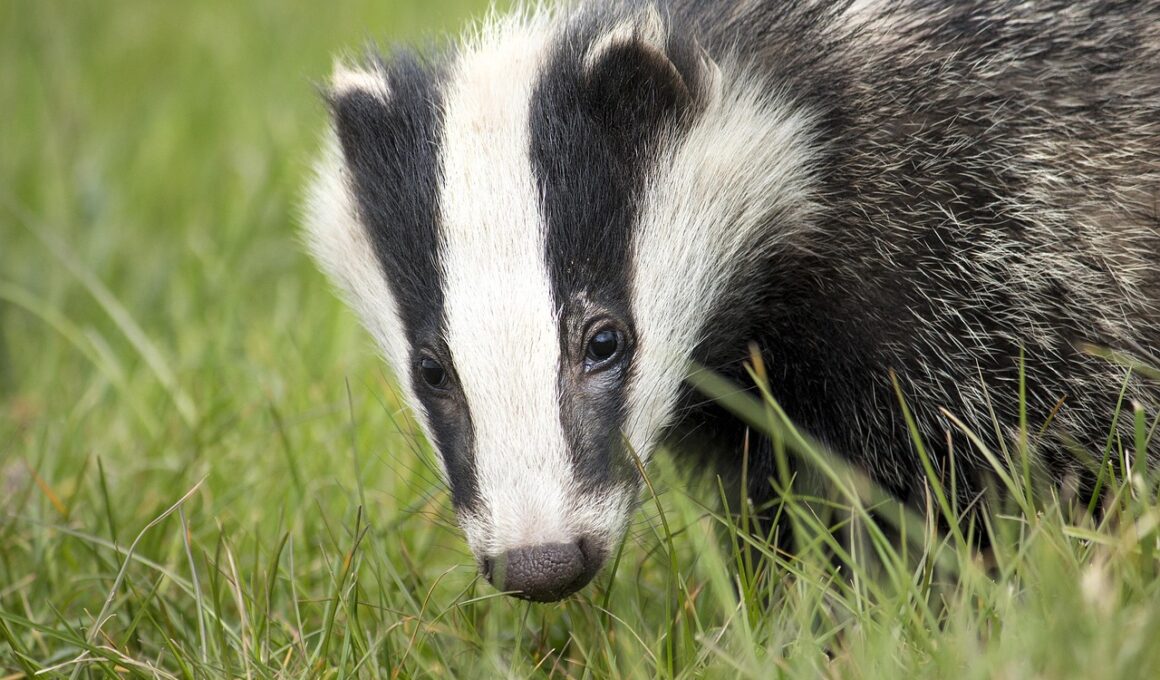
The Evolutionary History of Mustelid Badgers
Mustelid badgers belong to the family Mustelidae, which includes different carnivorous mammals. Understanding their evolutionary history offers profound insights into adaptation and survival. Badgers are a unique group of these animals that have developed specific traits suited to their environments. Historically, they have been found across various ecosystems, reflecting their diverse adaptations. As evolutionary processes unfolded, badgers adapted to changes in climate and habitat. The fossil record provides valuable evidence of evolutionary changes that led to modern mustelid species. Different species of mustelid badgers evolved in response to predation and competition. Their adaptations include changes in size, fur density, and dietary habits. Some species exhibit nocturnal behaviors to avoid predators and increase hunting efficiency. Genetic studies indicate that badgers share a common ancestor with weasels and otters and that divergence occurred as environmental pressures shifted. Additionally, their distinctive burrowing habits are essential for survival. Understanding these aspects sheds light on broader evolutionary trends within the Mustelidae family, including various adaptations that facilitate survival in diverse conditions. Mustelid badgers remain remarkable examples of evolutionary success amidst environmental challenges.
Badgers are known for their unique social structures as well, which adds complexity to their evolutionary story. Living in groups or clans influences reproductive strategies and social behavior among badgers. A defining feature of badgers is their burrowing tendency, using extensive tunnel systems primarily for shelter and protection. These systems often help them escape predators, creating advantageous survival conditions. Furthermore, their diets are varied, including insects, small mammals, and vegetation, showcasing their generalist feeding habits. This versatility likely contributed to their evolutionary success. Studies also reveal that badgers exhibit territorial behaviors, marking their ranges with scent in their communal living spaces. The relationship among clan members enhances cooperative hunting and pup-rearing efforts. Additionally, their physical adaptations, including strong limbs and robust claws, allow them to excavate efficiently. These factors altogether cultivate their resilience in changing environments over time. The social structures of badgers thus play a crucial role in their evolutionary history by promoting successful reproduction and survival strategies. Insights from their social dynamics highlight how cooperation may enhance fitness, shedding light on evolutionary theories regarding social behavior in wildlife.
Adaptations and Survival Strategies of Mustelid Badgers
Adaptations are fundamental for mustelid badgers in facing environmental challenges, demonstrating their evolutionary ingenuity. One significant adaptation is their specialized teeth and jaw structure, allowing efficient consumption of a varied diet. Their teeth are well-suited for tearing flesh and grinding tough plant material, enabling them to thrive in different habitats. In cold climates, dense fur provides insulation, while their fat reserves support energy needs during scarcity. Behavioral adaptations are equally critical; they exhibit seasonal changes in activity based on food availability and climate. Mustelid badgers have also developed unique strategies for avoiding predators, such as their ability to quickly retreat into their intricate burrows. This skill is vital for escaping larger carnivores that pose significant threats. Additionally, their nocturnal habits reduce the chances of encounters with many predators, thus enhancing their survival rates. Their keen sense of smell aids in locating food and detecting dangers. Furthermore, proficient digging skills enable them to find their prey underground or create safe shelters. All these adaptations together reflect a long history of evolution that has shaped how badgers interact with their environment, ensuring their continued existence among diverse ecosystems today.
Additionally, mustelid badgers play an essential role in their ecosystems, contributing to biodiversity and ecological balance. They help control insect populations, aiding other species in the food web. Their behavior facilitates seed dispersal, positively affecting plant communities. This ecological engagement highlights the interconnectedness of species and environments. These roles further underscore the necessity of preserving their natural habitats. Research has also shown that badgers can influence soil health through their foraging and burrowing habits. By aerating the soil, they enhance water infiltration and nutrient distribution, benefiting various plant species. Their burrows provide sanctuary for other smaller animal species, emphasizing their importance beyond their own survival. Moreover, studying their ecological impact allows scientists to assess changes in biodiversity and ecosystem health. Conservation efforts are often directed toward habitats where badgers live, aiming to protect them and their functions within the ecosystem. Through this lens, understanding their evolutionary history is crucial, not only for the species itself but for broader environmental preservation initiatives. As ecosystems face pressures from climate change and human activity, recognizing the value of mustelid badgers remains vital for maintaining balanced ecosystems across their ranges.
The Conservation Status of Mustelid Badgers
The current conservation status of mustelid badgers reflects both historical impacts and ongoing environmental challenges. Many badger species face declining populations due to habitat loss and fragmentation. Urbanization has drastically reduced their available habitats, leading to increased road mortality rates. Additionally, pesticide use poses risks, impacting their food sources and overall health. Conservationists are actively engaging in strategies to address these issues. Habitat restoration projects and wildlife corridors aim to reconnect isolated badger populations, allowing safe movement between areas. Public awareness campaigns educate communities on coexistence, seeking to reduce human-wildlife conflicts. Legal protections are in place in various regions, safeguarding mustelid badgers from hunting and habitat destruction. Research initiatives monitor populations and health status, contributing to conservation planning. Collaborations among governmental and non-governmental organizations enhance resource allocation for conservation efforts. It is crucial to understand local challenges facing badger populations, including interactions with domestic animals. Effective conservation must consider the landscape’s complexity to support the diverse needs of mustelid badgers. Sustaining their populations will require collective efforts to mitigate human impact and enhance habitat connectivity. Overall, the future of mustelid badgers remains interconnected with broader conservation strategies.
Education is a fundamental pillar in the conservation of mustelid badgers, fostering understanding and appreciation for these unique creatures. Schools, community organizations, and wildlife groups facilitate educational programs designed to inform about badger ecology and their role in the ecosystem. Engaging with the public increases awareness of the threats facing badgers, highlighting the importance of habitat conservation. Hands-on workshops and field trips allow individuals to observe badger behaviors in their natural habitats. Furthermore, educational materials targeting various age groups help to instill a sense of responsibility toward wildlife conservation. By promoting positive interactions with nature, communities can cultivate support for local conservation initiatives. Social media campaigns and documentaries have also gained traction in raising awareness about badger conservation. These platforms enable real-time engagement with broader audiences, emphasizing the narrative of survival amidst environmental challenges. The collaboration between educators and conservationists offers new opportunities to inspire legislation supporting mustelid populations. Ultimately, education drives change, encouraging individuals to advocate for sustainable practices that protect badger habitats. By nurturing an informed public, the future of mustelid badgers can be more assured, preserving their evolutionary legacy for generations to come.
The Future of Mustelid Badgers
Looking ahead, the future of mustelid badgers hinges on effective conservation efforts and research advancements. Addressing climate change remains a significant priority as it poses a looming threat to their habitats. As climate patterns shift, reliance on ecosystems shifts, directly impacting the food sources available to badgers. Adaptive management strategies can mitigate some effects, ensuring resilience within populations. Continued research will also provide insights into behavioral changes caused by environmental pressures. Genetic studies may identify how badgers can adapt to changing ecosystems, revealing vital information for conservation practices. Additionally, the integration of technology in wildlife monitoring offers innovative solutions for tracking badger movements. Using GPS collars allows researchers to gather data on their ranges and interactions with other species. Such information is pivotal in forming effective conservation policies that respond to emerging threats. Engaging local communities in these efforts fosters stewardship, establishing a collaborative approach to safeguarding mustelid populations. Education campaigns emphasize the importance of biodiversity and how every species contributes to ecological harmony. By thus prioritizing research and community engagement, we can ensure that mustelid badgers thrive, preserving their evolutionary history and ecological significance for the future.
In conclusion, understanding the evolutionary history of mustelid badgers encapsulates how their unique adaptations enable survival across diverse environments. From their physical characteristics to their social structures, these factors illustrate their resilience in facing ecological pressures. As we study these fascinating creatures, we learn about the broader implications of conservation efforts and the interconnectedness of our ecosystems. The threats faced by mustelid badgers underscore the urgent need for sustainable practices and habitat protection. With sincere efforts directed at preserving their populations, there is hope for maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity within their ranges. Advocacy and community involvement play critical roles in ensuring future generations can witness these magnificent animals. Conserving mustelid badgers is not merely about protecting a species but about maintaining the integrity of our ecosystems. Continued research, education, and community engagement are vital for fostering positive relationships with wildlife. As humanity navigates the complexities of environmental changes, commitment to conservation will be paramount in ensuring the survival of mustelid badgers. This evolutionary narrative reinforces the necessity for collective action to fathom the balance between human development and ecological preservation.