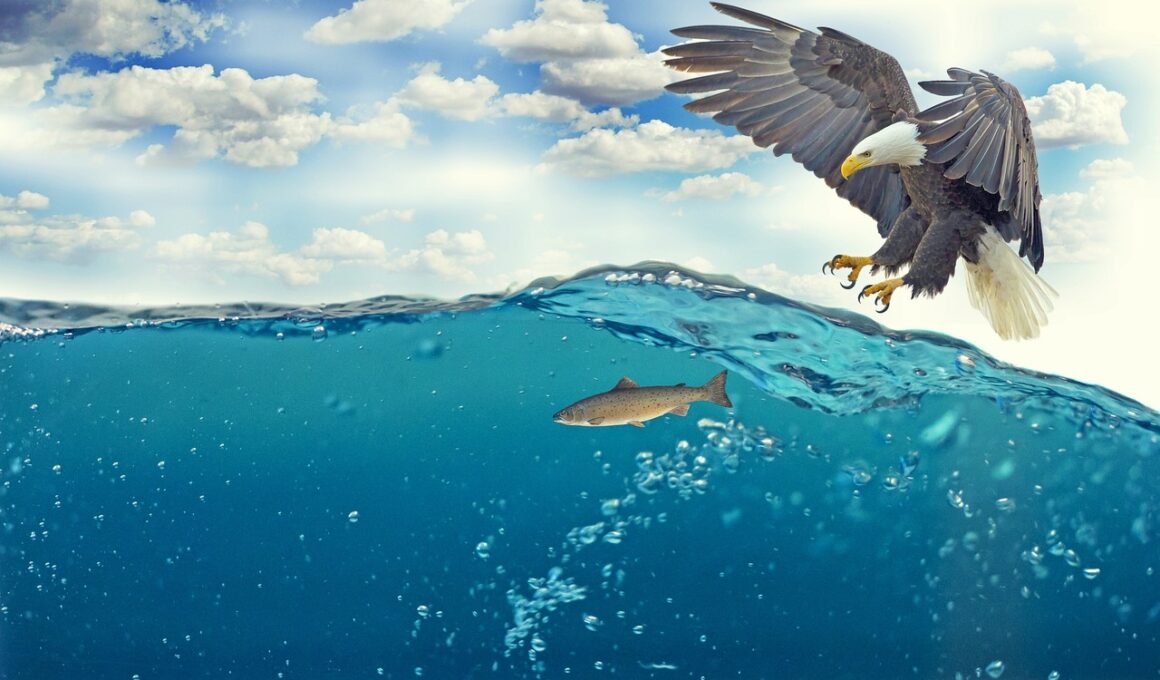
Impact of Climate Change on Predator Hunting Techniques
The ongoing effects of climate change profoundly influence predator hunting techniques across various ecosystems. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, the habitats of many predators are altered, forcing them to adapt to new circumstances. Changes in prey availability often ensue as climate-induced shifts lead to the migration of species to newer, more favorable environments. This results in altered feeding behaviors and hunting strategies among predators. Some organisms may search for prey during different times of the day due to temperature fluctuations or resource scarcity. Animal adaptations become essential as their prey responds by adapting to these environmental changes as well, creating a challenging chase for survival. Hunting techniques may include ambush strategies, social hunting tactics, or solitary pursuits, tailored to the circumstances presented by a shifting climate. The intricate balance between predator and prey is increasingly influenced by external factors such as weather extremes and ecological disturbances. Understanding these connections is crucial for conservation efforts aimed at protecting both mammals and their prey as they navigate this changing world.
This shift is especially notable in apex predators such as wolves, lions, and orcas, which play critical roles in their respective ecosystems. As prey populations decline due to habitat loss or altered migration patterns, these top predators face increasing challenges in securing food. For instance, wolves may adapt by hunting smaller, more numerous prey, which alters their pack dynamics and territorial behaviors. This adaptation to changing prey dynamics requires an intricate understanding of both biological instincts and environmental cues. Additionally, climate change may lead to the emergence of new species within a predator’s habitat, introducing new competition or prey options. These changes force predators to rapidly adapt their strategies to exploit scarce resources. Social structures within these animal communities may also shift due to altered hunting and foraging behaviors, affecting reproduction and population stability. Ultimately, the success of these species largely depends on their ability to adapt to the swiftly evolving climate along with the potential emergence of disease and genetic adaptations driven by these environmental stresses.
Effects on Foraging Behavior
Foraging behaviors are heavily influenced by climatic variables, which prompts necessary changes in predator hunting techniques. Temperature, precipitation, and seasonal shifts result in a direct impact on availability and distribution of prey. Predators often rely on cues from their environment to hunt efficiently and effectively. For example, warmer weather may lead to earlier emergence of prey species, requiring predators to adjust their hunting schedules accordingly. Changes in prey population densities can also force predators to explore uncharted territories. Such adaptations could prove beneficial or detrimental depending on how well each species can modify their traditional foraging strategies. Altered hunting times and locations are significant for maintaining energy efficiency, particularly in a world where resources become scarce. Unpredictable weather events and habitat destruction further complicate these adjustments, forcing predators towards less favorable hunting grounds. The interaction between multiple species across the food web adds complexity to the response seen among predators. As they navigate new environments, learning from each experience represents a critical factor for survival as they tackle the challenges posed by climate change head-on.
The shift in hunting strategies includes an increase in opportunistic feeding behaviors as predators adjust to the unpredictable availability of food. As climate change alters habitats, some species may find that traditional hunting territories become severely diminished. The necessity to diversify dietary options becomes apparent as previous staple food sources may no longer be accessible or abundant. This could lead to a shift towards scavenging behavior, enabling these predators to survive during tough times. On a larger scale, these changes in hunting behavior can influence ecological balance and promote competition among species that have previously coexisted peacefully. Adaptable predators are likely to thrive, while those unable to adjust may face severe survival challenges. In some regions, various predators may prey on the same dwindling populations, leading to increased competition and conflict. Therefore, understanding these behavioral changes is vital for wildlife management and conservation, as it helps predict which species may need assistance in adapting to or surviving in changing ecological landscapes caused by climate shifts.
Impact on Predator-Prey Dynamics
The complexities of predator-prey dynamics intensify as species adapt to the effects of climate change. The interplay between predators and their prey can lead to unexpected outcomes as each group reacts to changing environments. For instance, prey species may develop new defense mechanisms or behavioral adaptations to escape predation. These evolutionary responses can disrupt the established equilibrium within ecosystems, resulting in fluctuations in population numbers and community structure. This change may also lead to the emergence of new predator-prey interactions as species migrate to different areas. One of the significant challenges facing ecosystems is how effectively each species can adapt to the rapidly changing climate. Documenting these adaptations can help ecologists predict future interactions and fluctuations within these communities. Furthermore, understanding the ways in which climate change alters these dynamics is crucial for preserving biodiversity. Conservation strategies might require reevaluation to ensure that all species have the necessary resources, environments, and opportunities to thrive amidst climate-induced changes.
Ecologists increasingly recognize the need for comprehensive adaptation strategies to respond to these evolving relationships. In response to the shifts in habitat and food supply, many predators will need to rely on their innate abilities to adapt, learn, and innovate. This dynamic landscape calls for flexibility in hunting techniques and social behaviors. Increased human activities and land-use changes could further amplify these pressures, impacting food webs in profound ways. For some species, the pressures of climate change necessitate rapid changes in their life history patterns or hunting methods, creating a mosaic of responses across different ecological communities. Conservationists are tasked with identifying and prioritizing which species, populations, and habitats will require strategic support in adapting to this new reality. In some cases, this may involve habitat restoration or creating wildlife corridors that facilitate connectivity among fragmented populations, allowing those who are struggling to seek refuge. The future of many predators depends heavily on our ability to predict their responses to these shifting environments.
Future Implications for Wildlife Management
Looking ahead, climate change will continue playing a transformative role in shaping ecosystems and predator hunting techniques. The effects of changing climatic conditions call for immediate attention from wildlife management professionals who must adapt their strategies accordingly. This entails carefully monitoring both predator and prey populations to identify any shifts that can inform conservation policies. Implementing wildlife corridors can enhance the connectivity among target species’ habitats, increasing their chances of successfully navigating these transformations. Furthermore, understanding the behavioral shifts of predators can guide the development of research initiatives aimed at mitigating the adverse effects of climate change on various species. Engagement with local communities also represents an essential aspect of conservation efforts, as collaborative efforts can bridge the gap between wildlife management and local ecological knowledge. By empowering communities to participate in conservation, the chances of preserving biodiversity improve significantly. Continued investment in these adaptation strategies will be pivotal in ensuring the survival of both apex predators and their ecosystems in the face of ongoing climate change challenges.
The adaptive behavior exhibited by predators in response to climate change not only reflects their resilience but also signifies the larger shifts occurring within global ecosystems. Observing these changes provides important insight into how environmental factors drive evolution and behavioral adaptation. Wildlife managers must recognize the interconnectedness of all species and encompass conservation strategies that embrace this holistic perspective. Furthermore, fostering partnerships among researchers, policymakers, and local communities will allow for a more comprehensive understanding of these ever-changing dynamics. Engaging in long-term monitoring efforts will facilitate early interventions to protect vulnerable species as they face ongoing climate challenges. Ultimately, the interplay of predator hunting techniques and climate change serves as a poignant reminder of the necessity for prompt action to ensure the survival of biodiversity on our planet. Collaboration will be key in adapting to these changes and preserving the delicate balance of ecosystems crucial for all life forms.