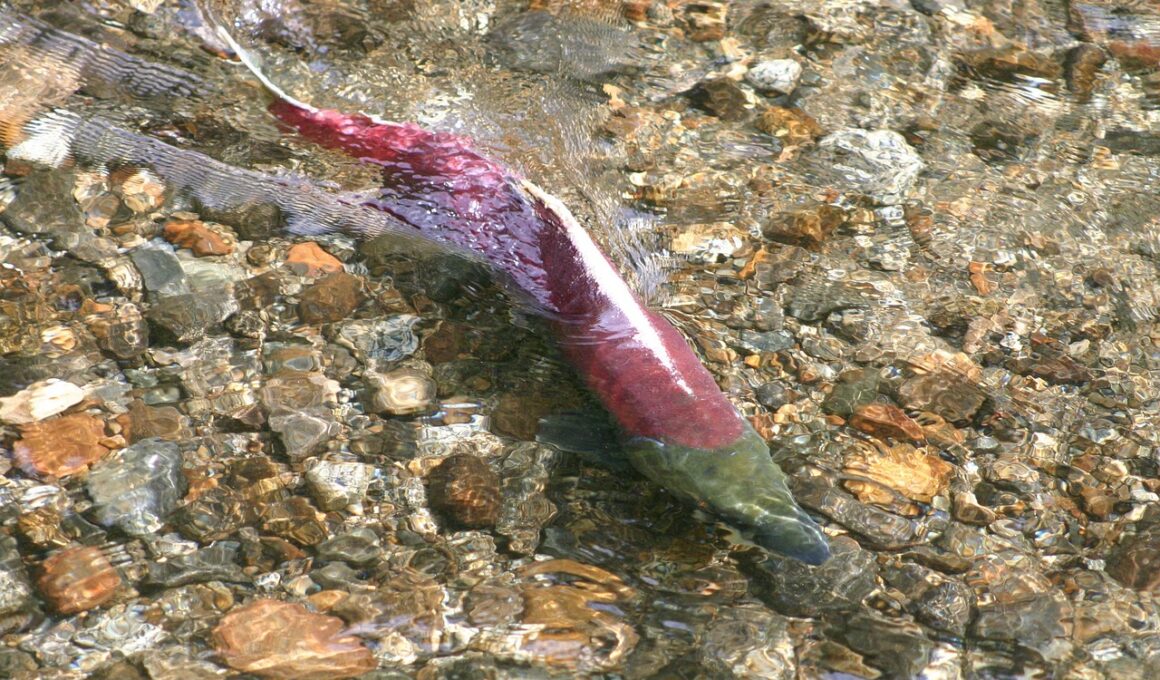
Understanding the Basics of Fish Migration Patterns
Fish migration patterns play a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring sustainable fish populations. Understanding these patterns is vital for conservation efforts and fisheries management. Fish migrate for various reasons, including spawning, feeding, and seeking suitable habitats. Each species exhibits its unique migration behavior, influenced by environmental factors such as water temperature, currents, and food availability. Migration can be categorized into several types:
- Latitudinal migration, where fish move north or south.
- Vertical migration, occurring in response to temperature gradients or light.
- Seasonal migration, when fish relocate due to changing seasons.
Moreover, migration can be influenced by obstacles such as dams and pollution, often disrupting established routes. Understanding fish migration patterns not only aids scientific research but also promotes better fishing practices, allowing populations to recover effectively. By conserving migratory routes and breeding grounds, stakeholders can enhance biodiversity and the overall health of aquatic ecosystems. Continued research into these patterns is essential for adapting to climate change and its effects on migratory fish species over time. Fish migrations are a fascinating subject that warrants further exploration and understanding.
The Importance of Migration for Fish Species
Migration remains vital for numerous fish species across global waters. It allows fish to access optimal environments for spawning, feeding, and growth. Without migration, many species would struggle to survive and reproduce effectively. For instance, salmon are well-known for their long migrations from freshwater rivers to the ocean and back again to spawn. Similarly, species such as eels undertake transcontinental migrations over thousands of miles. Different species have adapted to their unique migratory routes, leading to impressive evolutionary traits. Healthy migratory behavior ensures genetic diversity among populations, enhancing their resilience against diseases and environmental changes. Furthermore, these migratory patterns support local economies by sustaining fisheries that rely on seasonal fish populations. However, human activities like coastal development and pollution negatively impact migratory routes. Habitat loss and obstruction further hinder migration, which can lead to population declines. Therefore, maintaining habitats and implementing conservation efforts is critical for protecting fish migrations. Developing fishways and restoration projects can help restore natural migration paths. This ensures the survival of fish populations and fosters ecological balance in aquatic ecosystems that rely on these fish.
In addition to biological and ecological importance, fish migration patterns also have significant economic implications. Commercial fishing industries depend heavily on understanding these migrations to optimize harvests and sustain fish populations. Migratory patterns can lead to seasonal fish abundance, creating opportunities for fisheries to thrive. Accurate data collection and analysis of fish movements can inform regulatory measures, allowing sustainable practices to be established. Furthermore, the tourism sector benefits from fish migrations, especially during spawning events that attract anglers and nature enthusiasts alike. Notably, the migration of fish can enhance ecosystems by promoting nutrient cycling. Fish excrement and carcasses provide essential nutrients that promote productivity in marine and freshwater environments. The relationships between fish migration and economic sectors underline the importance of establishing comprehensive management strategies. Such strategies can foster cooperation among stakeholders, ensuring that fish populations are maintained while supporting livelihoods. Failure to recognize the intricacies of these interconnections may lead to overfishing and habitat destruction, jeopardizing both fish and human communities. Hence, long-term planning based on migration data is necessary for promoting ecological resilience and economic sustainability.
Challenges Facing Fish Migration
Several challenges confront fish migrations in today’s rapidly changing environment. Climate change plays a prominent role in altering spawning times, temperature ranges, and the availability of food sources. Specifically, warming waters can shift the distribution of fish populations, forcing them into unfamiliar territories. Additionally, increased rainfall and melting ice caps lead to altered river flows, which can impact migration routes. Pollution from urban runoff, plastics, and industrial discharges further complicates matters by reducing water quality and harming fish health. Other anthropogenic factors, such as dam construction and habitat destruction, can completely obstruct migratory paths. Some rivers, once thriving migratory corridors, have become impassable zones due to man-made barriers. Consequently, fish populations face heightened vulnerability to extinction due to disrupted migration. To mitigate these impacts, ongoing efforts must focus on restoring habitats and reducing barriers. Initiatives include constructing fish ladders or bypasses around dams and restoring wetlands to help facilitate fish movement. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration among scientists, policymakers, conservationists, and local communities. Only through concerted efforts can we secure the future of global fish migrations.
Research into fish migration patterns continues to evolve, employing modern technology and innovative methodologies. Tracking migratory movements has become increasingly precise with advancements in satellite and acoustic telemetry. These technologies enable researchers to monitor fish movements in real-time, providing valuable data on migration routes, timing, and spawning behavior. By equipping fish with transmitters, scientists can gather crucial information on their migratory habits and identify key habitats. Furthermore, genetic studies have shed light on the adaptability of fish populations in response to environmental changes. Understanding the genetic traits that drive migratory behavior can inform conservation strategies aimed at enhancing the resilience of fish populations. Data collected from these technologies can also assist in predicting future migration patterns, allowing stakeholders to adapt their management practices accordingly. Additionally, citizen science programs encourage public involvement, fostering awareness about local fish migrations. Community participation aids in data collection and helps develop stewardship over aquatic ecosystems. Overall, interdisciplinary approaches combining technology, genetics, and public engagement reveal a comprehensive understanding of fish migration patterns and facilitate informed decision-making for conservation efforts.
Conservation Strategies for Fish Migration
The conservation of fish migration patterns requires the implementation of multifaceted strategies that address the various threats they face. One effective approach involves habitat restoration, aimed at improving the quality and connectivity of migratory corridors. Reestablishing wetlands, reducing pollution, and removing obstacles can significantly enhance fish passage. Additionally, creating protected areas along migratory routes helps safeguard essential habitats from development or exploitation. Effective management plans should involve scientists, fisheries managers, and local communities to ensure diverse perspectives are considered. Research is essential to identify critical habitats and quantify the effects of altered flows and temperatures on fish populations. Furthermore, public education plays a crucial role in fostering an understanding of the importance of migration for ecosystem health. Engaging local communities in stewardship initiatives encourages sustainable fishing practices and habitat conservation. Legislative efforts must also support fish migration through policies that emphasize ecological considerations in development projects. Collaborative partnerships among governments, NGOs, and industry stakeholders are critical for implementing long-term conservation strategies. Collectively, these measures will help preserve fish migrations that are vital for maintaining biodiversity and supporting cultural and economic traditions.
Future Outlook for Fish Migration Research indicates that ongoing research will increasingly focus on understanding the impacts of global change on fish migration patterns. With the anticipated changes in climate, habitat loss, and ocean acidification, comprehensive studies will help predict how populations will adapt or relocate. Innovative technologies will continue to provide insights into fish behaviors, supporting the development of responsive conservation strategies. Moreover, a greater emphasis on interdisciplinary collaboration will pave the way for integrating ecological, social, and economic dimensions of fish migration. This includes the examination of cultural relevance and indigenous knowledge in fishing practices. By leveraging these diverse insights, stakeholders can foster resilience in fish populations as they navigate rapidly changing environments. Engagement with local communities indelibly ties the success of conservation efforts to cultural understandings and traditional practices. The future of fish migration research promises exciting advancements that will deepen our comprehension of aquatic ecosystems. Observational studies combined with modeling efforts can help foresee possible scenarios, ultimately guiding proactive management. The knowledge gained through research will shape policies that ensure the sustainable coexistence of fish populations and human activities, fostering a harmonious balance.