Understanding the Hydration Needs of Different Animal Species
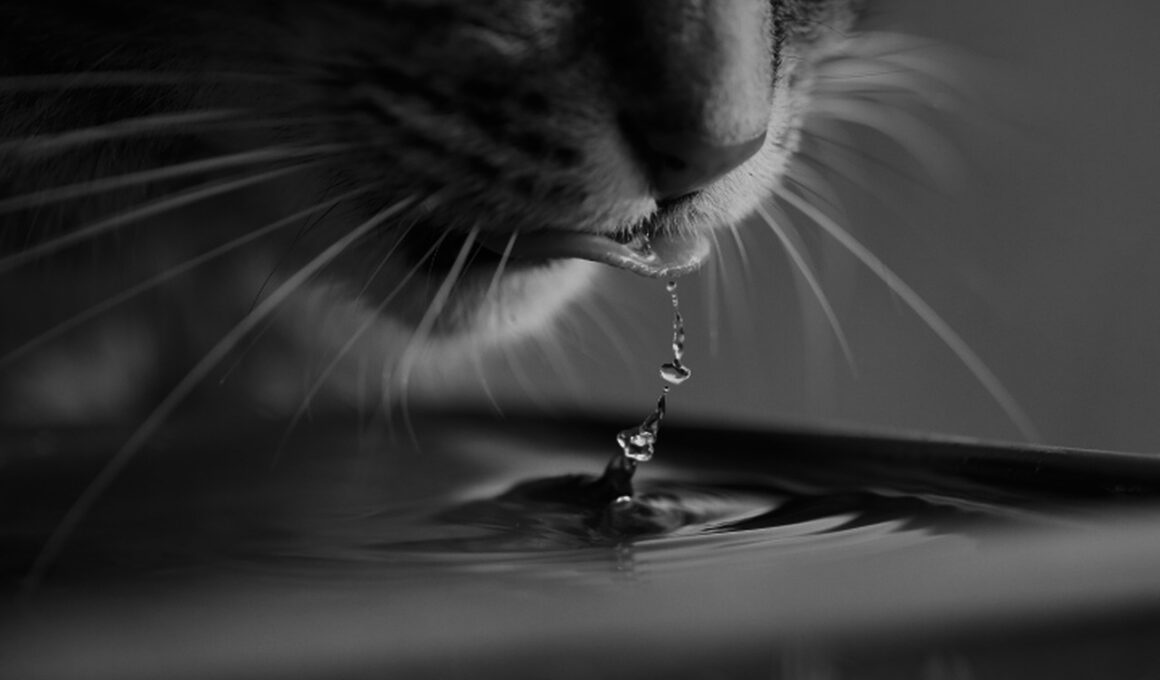
Proper hydration is crucial for all animal species, affecting their overall health and well-being. Each species has different hydration requirements based on factors like size, activity level, age, and environmental conditions. For instance, large mammals such as elephants need vast amounts of water daily, while smaller animals may require less. Additionally, animals in warmer climates often require more water. Animals such as cats and dogs rely heavily on water sources, which can vary between species. It’s vital for pet owners to ensure their pets have access to fresh water at all times. In wild settings, animals instinctively travel to water sources, but urban environments may complicate this. Understanding these differences helps in fostering responsible pet ownership and wildlife conservation. Furthermore, the composition of the diet can influence hydration; animals that consume high moisture food, such as fruits and vegetables, may need less water. Knowledge of these dietary habits is essential for wildlife rehabilitation efforts and effective veterinary care. Overall, proper hydration can prevent health issues related to dehydration and improve the quality of life for both wild and domesticated animals.
In addition to access to fresh water, various species have notable differences in how their bodies utilize water. Some animals, like kangaroos, can extract moisture from their food more efficiently, allowing them to thrive in arid environments. Others, such as camels, have specialized adaptations that help them conserve water, enabling survival in extreme desert conditions. Whereas many animals will instinctively drink from available sources, reptiles often absorb moisture through their skin or directly from their food. This diverse array of adaptations highlights the incredible ways that different species meet their hydration needs. Moreover, certain physiological factors, including activity levels and metabolic rates, play significant roles in determining hydration requirements. For example, working dogs or animals engaged in physical labor may require more fluids than less active companions. Monitoring water intake is essential, as dehydration can lead to severe health issues like kidney disease or urinary problems. Furthermore, during hotter seasons or periods of high activity, animals must have increased access to hydration sources. Ensuring that animals remain properly hydrated contributes significantly to their overall health and vitality, enabling them to live longer, happier lives.
Influence of Environment on Animal Hydration
The environment plays an essential role in determining the hydration levels of various animal species. Different habitats present unique challenges and opportunities for hydration, affecting how animals obtain and conserve water. In humid climates, many species benefit from abundant natural water sources, allowing easy access to hydration. For example, rainforests host a variety of species that rely on abundant moisture in their surroundings. Conversely, creatures adapted to desert environments develop unique strategies to minimize water loss. Animals that inhabit such harsh conditions often have diminished thirst instincts, allowing them to avoid dehydration by reducing water consumption. Behavioral adaptations also come into play—for example, nocturnal animals may choose to be active during cooler night hours to reduce water loss through respiration. Furthermore, migratory species often follow water sources during seasonal movements, demonstrating the interconnectivity of habitat and hydration. The adaptation to various environmental factors underscores the importance of protecting natural ecosystems for wildlife. Conservation efforts should prioritize maintaining these habitats to ensure all species possess sufficient access to water. Understanding how the environment impacts hydration can better inform wildlife management practices.
Understanding the hydration needs of domesticated animals is equally important, particularly for pet owners and farmers. Pets like cats and dogs should have regular access to clean drinking water. Moreover, pet owners should monitor their pets for signs of dehydration, such as lethargy or a dry mouth, and understand how factors like weather and exercise levels might change their hydration needs. It’s not just enough to provide water—ensuring that the water is fresh and safe is critical. Farmers with livestock must also pay attention to the hydration needs of their animals, especially during hot weather or times of increased activity. Animals such as cattle and sheep can suffer significantly from dehydration due to heat stress if adequate water is not provided. Additionally, livestock diets can impact hydration; feeding animals high-salt foods may increase their need for water. Farmers should be proactive in observing behavioral cues and adjusting water supplies accordingly. Implementing effective hydration management practices aids in promoting livestock health and productivity. Educated care leads to a higher quality of life for domesticated animals in both agricultural and household settings.
Impacts of Diet on Animal Hydration
The diet of different animal species significantly influences their hydration needs and overall well-being. Some animals obtain a considerable amount of their needed hydration through the food they consume. Herbivores such as deer or rabbits tend to eat high-moisture vegetables and fruits, allowing them to achieve adequate hydration without requiring large quantities of additional water. Conversely, carnivorous animals may consume dryer meats, necessitating increased water intake alongside their diet. Understanding these dietary preferences can help ensure that animals receive adequate hydration. For example, animals fed kibble may require more water, whereas those consuming wet food may need less. In addition, the salt content in an animal’s diet directly impacts water needs. Animals that consume high-salt foods will subsequently require more water to stay adequately hydrated. Pet owners are encouraged to read food labels, understanding how nutritional content relates to hydration needs. Veterinarians can provide guidance on appropriate diet choices to support hydration effectively. Knowledge of how diet correlates with hydration helps us ensure that both domestic and wild animals are healthy and well-hydrated, which is crucial for their overall health and functionality.
Another crucial aspect of animal hydration is monitoring and assessment of water quality. Different species are sensitive to various contaminants, which can severely impact their hydration and overall health. For example, livestock drinking from stagnant water sources can be exposed to harmful bacteria and parasites. Such exposure can lead to infections or even more severe complications. Keepers should regularly test water quality, especially for ponds or streams utilized by wild animals. Moreover, wildlife conservationists often utilize clean, natural water sources in their habitat restoration efforts to support animal health. In addition, the importance of human impact on water sources cannot be understated. Urbanization, pollution, and climate change each influence natural water availability. Animals may face dehydration due to the contamination of former water sources. Therefore, efforts to protect water quality in both urban and rural settings are essential in promoting healthy ecosystems. Comprehensive management of water quality draws a clearer line to animal hydration success. By addressing the importance of clean, accessible water, we support diverse ecosystems and ensure health resilience for all animal species.
Conclusions on Animal Hydration
Understanding the hydration needs of different animal species unlocks a wealth of information vital for their comprehensive care. Both wild and domestic animals rely on fresh water availability to maintain their health and energy levels. Through studies of behaviors, dietary patterns, and environmental adaptations, we learn about the varied strategies animals employ to stay hydrated. By monitoring various factors influencing hydration, including diet, environmental conditions, and behavioral traits, we can formulate responsible care practices for pets and livestock alike. As society advances, awareness and attention to the importance of hydration in animals should grow. Providing accessible, clean water becomes imperative in minimizing health-related issues such as dehydration or heat stress. Furthermore, proactive measures in environmental conservation and habitat maintenance support the hydration needs of wild species. Education for pet owners, farmers, and wildlife advocates significantly impacts animal health and well-being. By prioritizing hydration, we elevate the standard of care given to various animal species, enhancing their quality of life. Ultimately, understanding these insights allows us to foster more compassionate and effective stewardship of all animals within our care and in the wild.
Adopting practices that promote proper hydration can lead to significantly happier, healthier animals, thereby providing them with better chances for longevity. To nurture an environment that supports animal hydration, we must advocate sound agricultural practices, thorough veterinary care, and conscientious wildlife management. Incorporating moisture-rich diets whenever possible enhances hydration for a large variety of animals. As we develop deeper insights into each species’ unique hydration needs, we will continue to refine our approaches to care. Furthermore, public awareness of the water-intensive needs of animals plays a key role in driving conservation efforts. By creating informative campaigns, organizations can help individuals understand the importance of maintaining safe water sources. These endeavors contribute to broader environmental health initiatives, ensuring long-term victories for both wildlife and domesticated animals alike. Finally, involving local communities in water purification and conservation work can enhance the well-being of animal populations. These shared responsibilities bolster our impact on healthy ecosystems, benefiting everyone involved in the conservation cycle. Such a comprehensive approach builds shared knowledge that can create a brighter future for all animal species, ultimately ensuring they thrive on our planet.