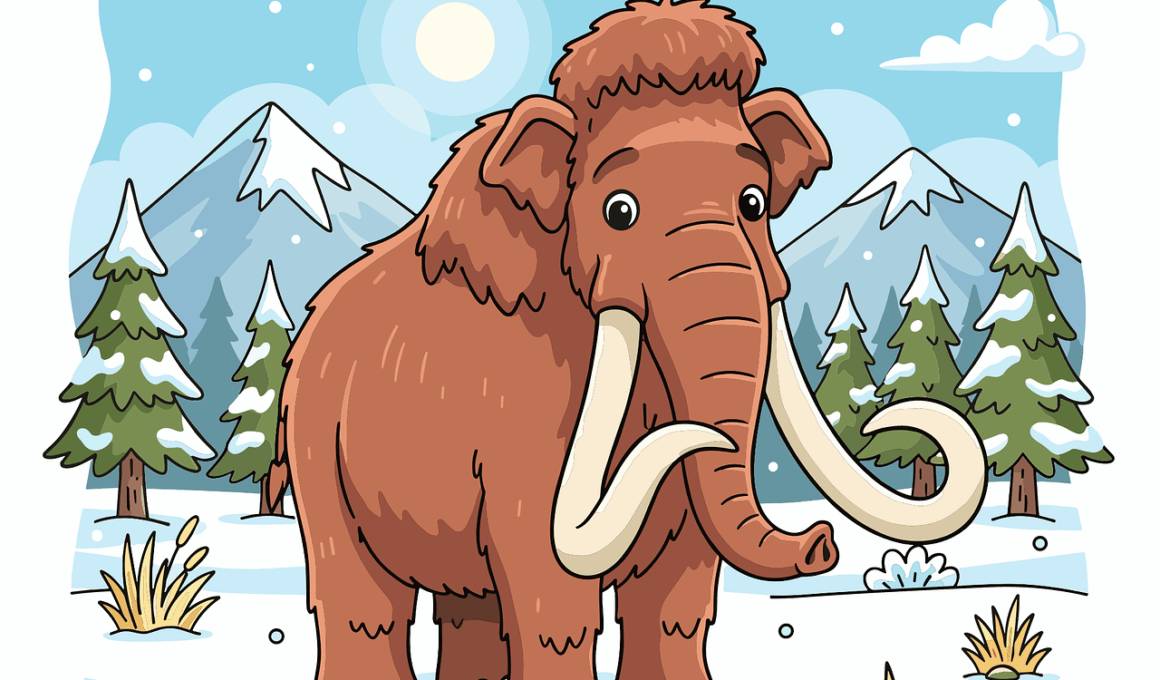
Woolly Mammoth Habitat and Lifestyle
The Woolly Mammoth, scientifically known as *Mammuthus primigenius*, was once a majestic creature inhabiting the cold tundras of the northern hemisphere. These large herbivores thrived in environments characterized by grasslands and sparse forests. Their habitats were typically located in areas that experienced harsh winters, and they roamed vast distances to find food and suitable conditions. Woolly Mammoths were well-adapted to these chilly climates thanks to their thick fur, which consisted of long, coarse outer hairs and a dense undercoat. They relied on their massive tusks, which could reach up to 15 feet in length, to dig through snow to access vegetation. Furthermore, they often traveled in herds, facilitating social interaction and protection against predators. Their unique habitat meant that they frequently migrated to locate adequate food supplies, such as grasses, shrubs, and other plant materials available in the tundra regions. As a result, Woolly Mammoths were integral to these ecosystems, serving as herbivores that influenced vegetation patterns and soil composition. Understanding their habitat helps us learn more about their lifestyle and the environmental challenges they faced during the Ice Age.
The social structure of Woolly Mammoths was likely complex, with herds consisting of related females and their young. Males would typically leave the herd upon reaching maturity, usually around 10 to 12 years of age. Within these herds, females exhibited cooperative behaviors, which played a significant role in nurturing and protecting the young. These interactions allowed them to maintain a strong community bond, crucial for survival in the harsh conditions of the tundra. The herding behavior also provided safety in numbers, protecting against predators like saber-toothed cats and humans who hunted them for food. Communication among Woolly Mammoths was essential; they likely used a combination of sounds, such as trumpeting calls and low rumbles, to convey messages about danger or locate each other in snowy landscapes. Moreover, their social behavior underscored their adaptability in challenging habitats, allowing them to share knowledge regarding migration routes and food sources. As these animals roamed expansively, they impacted the biodiversity of their ecosystems, contributing to a rich array of flora and fauna that thrived alongside them. Their extinction raises important questions about social structures in animal populations.
Diet and Feeding Habits of Woolly Mammoths
The Woolly Mammoth primarily fed on a variety of plant materials, significantly impacting their environment. Their diet consisted mainly of grasses, which were abundant during the Ice Age, but they also consumed shrubs, herbs, and even trees in some regions. Woolly Mammoths possessed large molars, specially adapted for grinding down tough vegetation. They were grazing animals, frequently foraging across vast distances in search of their preferred food sources, which could be unevenly distributed depending on seasonal conditions. This feeding habit played a critical role in the maintenance of their habitats by preventing shrub overgrowth, allowing diverse plant species to flourish. Additionally, their adaptations for cold climates and high-caloric diets meant that they had to consume large amounts of food daily, necessitating their migratory lifestyle. Woolly Mammoths were also likely to engage in a behavior called *facultative feeding*, altering their diet depending on the available vegetation, ensuring survival even during leaner times. This flexibility is a testament to their evolutionary adaptations to changing environments and resource availability in the tundra ecosystem. Their feeding habits also point to their ecological significance in shaping the landscapes they inhabited.
The extinction of the Woolly Mammoth has puzzled scientists for decades, leading to various theories about the causes. Climate change played a crucial role, as the end of the last Ice Age led to significant shifts in their habitat conditions, reducing their food supply. As the climate warmed, the grasslands and tundras that supported their diets diminished, replaced by forests that were less favorable for grazing. Additionally, human activity, particularly hunting, further exacerbated their decline. As early humans migrated into their territories, competition for resources and hunting intensified, leading to decreased populations. A combination of these factors is believed to have culminated in their extinction approximately 4,000 years ago. It’s essential to study not only their biological characteristics but also the environmental factors surrounding their disappearance. Restorative ecology and conservation efforts can benefit from understanding these dynamics while applying lessons from the Woolly Mammoth’s extinction to modern wildlife issues. The insights gleaned offer Valuable perspectives on resilience, adaptation, and the potential impacts of climate change on contemporary species facing similar threats in rapidly changing environments.
Fossil Evidence and Research
Fossils and preserved remains of Woolly Mammoths have provided valuable insights into their lives and habitats. For instance, many specimens have been discovered in the Siberian permafrost, where freezing conditions preserved their remains remarkably well. Researchers have unearthed bones, hair, and even soft tissues, allowing for in-depth studies of their physiology and behavior. These findings have enhanced our understanding of their evolutionary history, morphology, and interactions with the changing environment. Moreover, advancements in DNA analysis have enabled scientists to extract genetic material from these remains, leading to breakthroughs in studies of extinction, adaptation, and potential de-extinction efforts. For example, researchers are now exploring hybridization techniques that could use close relatives, like Asian elephants, to recreate Woolly Mammoth traits, aiming to understand the potentials of reintroducing these animals or their traits into current ecosystems. Though complex and controversial, this research could shed light on the ecological roles these creatures once played and their compatibility with modern environments. Fossil records also detail their migratory habits and provide evidence of how they adapted to changing climates, enriching our comprehensive knowledge of this fascinating extinct species.
In popular culture, the Woolly Mammoth has emerged as an iconic symbol of prehistoric life. They frequently appear in television shows, movies, and literature depicting the Ice Age, capturing the imagination of viewers with their massive size and distinctive fur. Their majestic appearance, combined with the mystery of extinction, makes them an enduring subject of interest. Exhibits featuring Woolly Mammoth fossils can be found in many natural history museums worldwide, allowing the public to engage with their history and understand the significance of these extraordinary animals within ecological contexts. Moreover, educational programs highlighting the lessons learned from their extinction foster awareness about the importance of conservation in preserving modern biodiversity. Artists and filmmakers have also utilized their forms for creative storytelling, often portraying them in fictional narratives that do not strictly adhere to scientific accuracy. This blending of fact and fiction can inspire a greater curiosity about the natural world, as well as the forces threatening our planet’s delicate balance. Popular culture plays a crucial role in keeping the story of the Woolly Mammoth alive. It engages the public and encourages discussion about extinction and biodiversity today.
Legacy of the Woolly Mammoth
The Woolly Mammoth’s legacy transcends its extinction, impacting both biodiversity studies and conservation efforts today. Emblematic of past ecological resilience, these animals serve as reminders of the implications of climate change and habitat disruption. By reminding us of the consequences of environmental shifts, the extinction of the Woolly Mammoth can inform modern conservation strategies aimed at preserving endangered species experiencing similar threats. Furthermore, they highlight the significance of maintaining genetic diversity within populations, which is crucial for adapting to changing environments. As researchers continue to uncover new findings about these magnificent creatures, they provide pressing lessons about human impact on ecosystems and the fragility of life on Earth. The discussions surrounding Woolly Mammoths open avenues for exploring how we engage with our planet and the responsibility we hold as stewards of the environment. Additionally, innovative technologies in genetic research not only deepen our understanding of extinct species and their adaptations but may present future possibilities for moderating contemporary biodiversity loss. Their story encourages introspection about our actions today and the importance of monitoring practices that ensure healthy ecosystems and species survival for generations to come.
In conclusion, the Woolly Mammoth embodies the intricate relationship between species and their environments. Their adaptations to cold habitats, migratory behavior, and complex social structures offer vital insights into survival strategies during challenging climatic conditions. The lessons learned from their existence are increasingly relevant in today’s context of rapid ecological changes. Understanding the Woolly Mammoth’s lifestyle enhances our grasp of prehistoric biology, contributing to environmental sciences and conservation efforts. The combination of archaeological evidence, fossil analysis, and genetic studies provides a comprehensive picture of their adaptation and extinction. Their legacy continues to ignite curiosity and fosters discussions about extinction and biodiversity preservation. By acknowledging the causes of their disappearance, we can strive to avoid similar fates for today’s endangered species. Ultimately, the Woolly Mammoth’s story serves as a critical reminder of the intricate web of life and the need for proactive measures to safeguard our planet’s biodiversity. As humanity grapples with ongoing environmental challenges, the tale of the Woolly Mammoth asks us to reflect on our connection to nature and our role in ensuring the survival of future generations.