Understanding the Respiratory System in Domestic Animals
The respiratory system in domestic animals plays a vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being. This system is responsible for the exchange of gases, facilitating oxygen intake while removing carbon dioxide. Various components constitute the respiratory system, including the nasal passages, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Each part is designed for specific functions to support respiration efficiently. In domestic animals like cats, dogs, and horses, this system adapts to different needs based on their activity levels and environmental conditions. For example, horses have larger physiological structures to support their larger oxygen demands during exertion. Distinct breathing patterns can also indicate stress levels when it occurs during exercise or other events. Proper understanding of these mechanisms can aid in early diagnosis of respiratory illnesses. Veterinarians rely on examining the respiratory rates and lung sounds to determine possible issues. Furthermore, recognizing abnormal signs can lead to timely interventions. Owners should also be knowledgeable about the symptoms of respiratory distress. Regular check-ups and attentive observation are essential for maintaining respiratory health, ensuring that their beloved pets lead active, comfortable lives.
Components of the Respiratory System
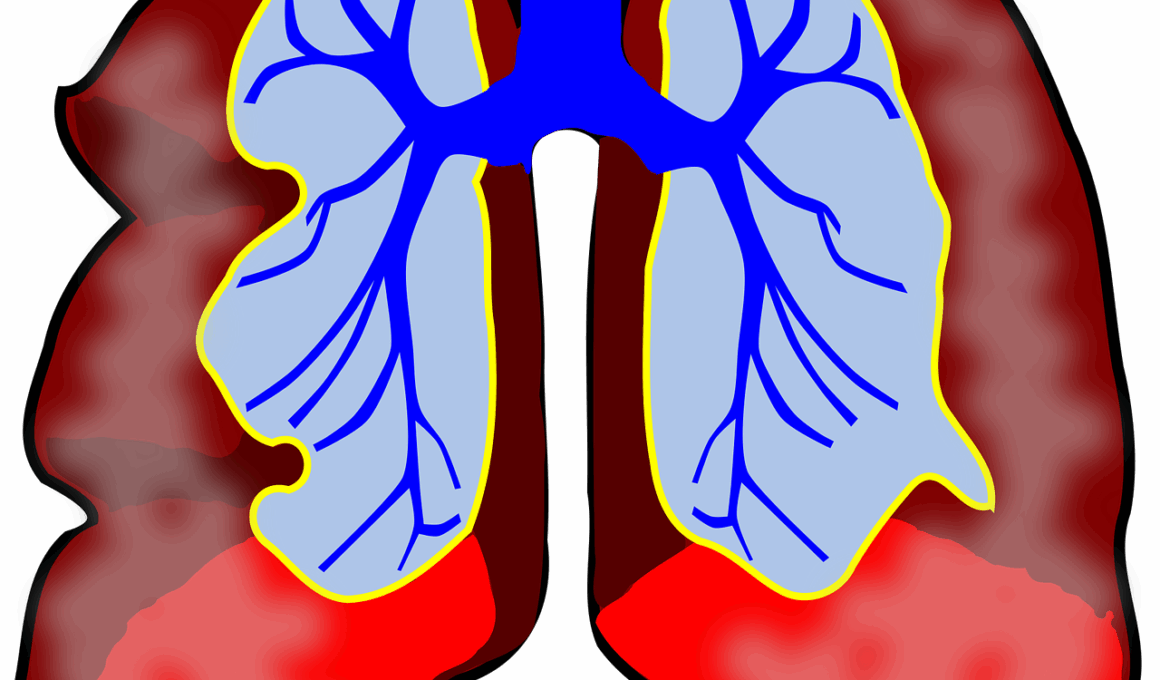
The respiratory system comprises various parts, each contributing to effective respiration. It begins with the nose, where air is filtered, moistened, and warmed before reaching the lungs. Following this, the trachea serves as a passageway for air to travel down into the bronchi, which branch into each lung. The lung lobes further branch into smaller bronchioles, extending into an intricate network of air sacs called alveoli. These alveoli are where the critical exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs. The efficiency of this exchange is influenced by the overall health of the lung tissue and adequate ventilation. Conditioning of inhaled air prevents pathogens and irritants from entering the lungs. Mucous membranes within the nasal passages contribute to this protection, trapping particles and preventing infections. Additionally, cilia, tiny hair-like structures lining the airways, help to move debris away from the lungs. Understanding these components is essential for recognizing how diseases like asthma or pneumonia can disrupt normal functioning. Attention to these details can be crucial in providing optimal care and preventing respiratory issues in domestic animals.
Respiration in domestic animals is categorized into two key phases: inhalation and exhalation. Inhalation occurs when the diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract, expanding the thoracic cavity and allowing air to fill the lungs. During this phase, oxygen-rich air is drawn into the alveoli for gas exchange. Conversely, exhalation is a passive process, wherein the diaphragm relaxes, and lung pressure expels carbon dioxide-laden air out of the body. Factors influencing respiration include age, size, fitness level, and environmental conditions. For instance, in hot weather, animals may breathe faster to regulate body temperature. Additionally, certain breeds exhibit unique respiratory traits, impacting their ventilation efficiency. Flat-faced breeds, such as Bulldogs, may experience difficulties due to their shorter airways and increased likelihood of airway obstruction. Understanding these variances assists veterinarians in creating tailored care plans for individual pets. Conditions such as chronic bronchitis or respiratory infections can severely affect these processes, leading to more severe health issues. Awareness of normal respiratory rates offers a baseline for pet owners, enabling early intervention when necessary. Observing changes in respiratory patterns can reflect overall animal well-being.
Common Respiratory Conditions
Domestic animals are susceptible to a variety of respiratory diseases that can significantly impact their quality of life. Common ailments include allergies, bronchitis, pneumonia, and infections caused by bacteria or viruses. Allergies often present with symptoms such as coughing, sneezing, and nasal discharge. In many cases, irritants like dust, smoke, or pollen can provoke these allergic reactions. Additionally, exposure to cold air can exacerbate existing respiratory conditions. Bronchitis, characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, can restrict airflow and make breathing painful. Pneumonia is a severe condition that leads to fluid accumulation in the lungs, making gas exchange difficult. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment of these conditions, as untreated respiratory issues can progress into chronic illnesses, significantly affecting the animal’s health. Owners should monitor their pets for signs of respiratory distress, including labored breathing or lethargy. Routine veterinary check-ups can aid in identifying and managing these conditions before they worsen. Preventative care and vaccinations can also reduce the incidence of respiratory infections, contributing to healthier, longer lives for domestic animals.
Effective treatment for respiratory conditions often requires a multi-faceted approach. Veterinary assessments typically include a thorough physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to determine the underlying cause. Depending on the diagnosis, treatment options may vary, from anti-inflammatory medications to antibiotics, depending on whether the condition is viral or bacterial. In allergic cases, antihistamines or corticosteroids may help alleviate symptoms. Maintaining an environment with good air quality is vital; minimizing dust and ensuring proper ventilation can help prevent respiratory issues from developing. Regular exercise can also strengthen the respiratory system by improving overall cardiovascular fitness and lung function. However, care should be taken to avoid exposing pets to extreme weather conditions. Nutritional support plays a critical role in maintaining the immune system, helping prevent infections. Additionally, providing pets with a stress-free environment reduces the risk of respiratory distress. Pet owners are encouraged to recognize warning signs early, such as persistent coughing or changes in behavior, to facilitate prompt veterinary care. Knowledge about respiratory health is crucial for the prevention and management of respiratory conditions in our beloved pets.
Preventative Measures for Respiratory Health
Preventing respiratory issues in domestic animals involves a combination of proactive care and awareness. Regular veterinary check-ups allow for early detection of potential problems and timely intervention. Vaccinations against common viruses and respiratory pathogens are essential to shield pets from infections. Maintaining proper hygiene, including regular cleaning of living spaces and bedding, helps minimize exposure to allergens and bacteria. Pet owners can implement air purifiers to enhance air quality, especially in homes with multiple indoor pets. Monitoring the living environment for irritants, such as smoke or chemical fumes, is crucial to create a safe space for pets. Additionally, seasonal allergies should be managed by bathing pets regularly to remove pollen and other allergens from their coats. Adequate hydration is vital for maintaining mucous membranes’ health and promoting effective respiratory function. Recognizing symptoms of distress such as shallow breathing or coughing can lead owners to seek immediate veterinary help. Understanding breed-specific concerns is essential for tailored preventive measures, as some breeds are more prone to respiratory difficulties. By fostering respiratory health through attentiveness and preventive care, pet owners ensure their animals lead healthy, active lives.
In conclusion, understanding the respiratory system in domestic animals is essential for promoting better health outcomes. Awareness of its structure, function, and potential risks empowers pet owners to engage in proactive care. Recognizing the signs of respiratory distress and maintaining a clean living environment equipped with fresh air enhances overall well-being. Regular veterinary visits ensure timely intervention and vaccinations protect against common infections. Treatment strategies should be devised based on the specific needs of each animal; customization is crucial to achieving optimal health. Additionally, educating oneself about breed-specific issues can prevent unnecessary suffering. Communication with veterinarians and acquiring reliable information are fundamentals in managing respiratory health. Engaging in a preventative approach, pet owners contribute significantly to their animals’ longevity and quality of life. Besides the physical health aspects, addressing behaviors arising from respiratory issues, such as anxiety, shows a comprehensive understanding of domestic animal care. Ultimately, responsible pet ownership involves shining a light on the intricate workings of the respiratory system, fostering healthier lives for pets within our homes. A robust commitment to respiratory health allows our beloved companions to thrive.