Diabetes Mellitus in Cats: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Diabetes mellitus is a serious health condition affecting many cats. It occurs when the feline pancreas cannot produce enough insulin, which leads to high blood sugar levels. Risk factors for diabetes in cats include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and advancing age. When cats gain extra weight, their bodies may develop insulin resistance, making it difficult for insulin to effectively lower blood sugar. If not managed properly, diabetes can lead to severe health implications over time. It is vital for cat owners to understand the nature of this disease to provide appropriate care. Cats exhibiting the following symptoms may require a veterinarian’s assessment: excessive thirst, increased urination, weight loss, and increased appetite. Regular check-ups can help detect diabetes early, allowing for better management and outcomes. Other underlying health conditions may also trigger diabetic symptoms, so comprehensive assessments are crucial. With appropriate care, many diabetic cats can lead happy, healthy lives. Understanding diabetes in cats can empower pet owners to make informed decisions about their feline companions’ health and wellbeing, reducing the risks associated with this condition.
To understand diabetes in cats, one must first recognize the role of insulin. This hormone helps regulate blood sugar by facilitating the entry of glucose into cells for energy. When diabetes occurs, either the pancreas fails to produce insulin or the cat’s body does not respond appropriately to it. This disruption leads to hyperglycemia, or elevated blood glucose levels. The consequences of untreated diabetes can be devastating; prolonged high blood sugar wreaks havoc on the body. Various body systems can become damaged severely, leading to problematic conditions such as neuropathy or liver disease. Identifying diabetes symptoms early can provide critical information to veterinarians, aiding in swift diagnosis and treatment. Owners must be vigilant for signs of excessive thirst and urination, which are common in affected cats. Since diabetes can significantly impact a cat’s quality of life, timely medical intervention is essential. After diagnosis, further tests may be ordered by a veterinarian to assess the severity and determine treatment options. It’s important to consult a veterinarian if any signs noted above are evident so that prompt action can be taken for the feline’s health.
Diagnosis of Diabetes in Cats
The diagnosis of diabetes in cats typically involves a combination of clinical symptoms, blood tests, and urine analyses. Initially, a veterinarian will conduct a thorough physical examination and inquire about observed symptoms. Blood tests can measure glucose levels to check for hyperglycemia. A consistent elevation in blood sugar, alongside the presence of glucose in urine, is indicative of diabetes. Additional diagnostics may include assessments of the cat’s overall health and potential underlying conditions since symptoms may overlap with other illnesses. After a definite diagnosis, a tailored treatment plan is crucial for managing the disease. It’s essential to closely monitor the cat’s blood sugar levels so adjustments can be made to the treatment plan as necessary. Owners should be prepared for lifestyle changes and possible dietary modifications recommended by veterinarians. Engaging in regular check-ups ensures progress is monitored effectively and concerns are addressed immediately. Early diagnosis also contributes to better management of diabetes, ultimately leading to improved quality of life for the cat.
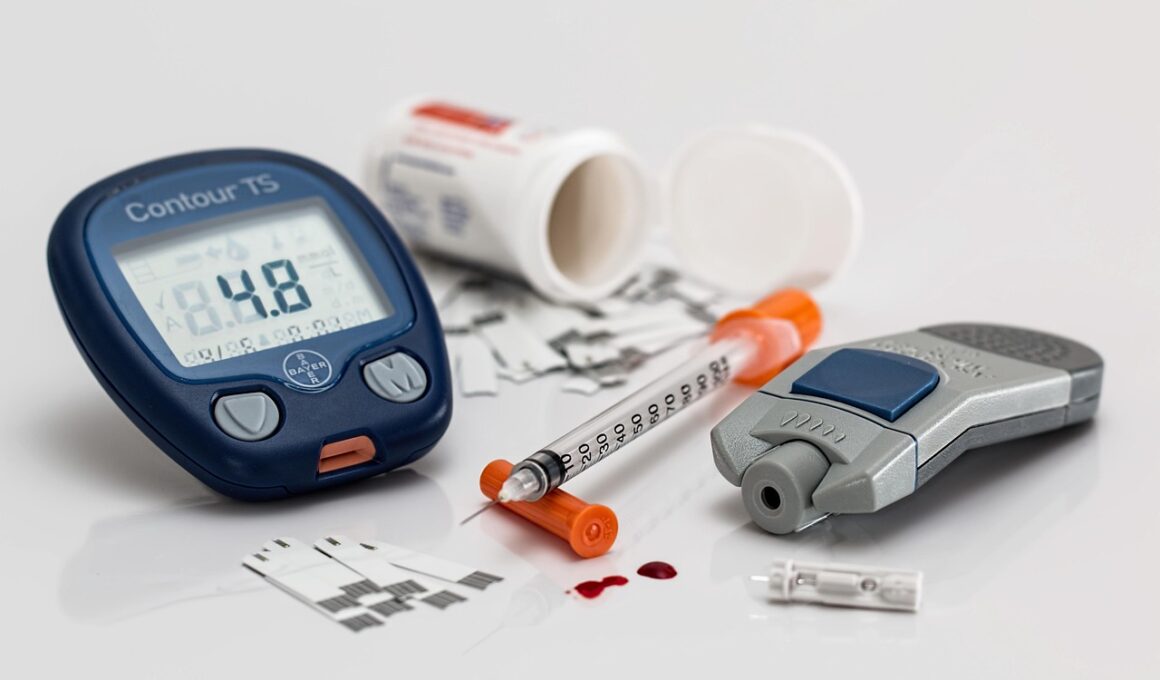
Managing diabetes in cats requires a comprehensive approach tailored to each individual cat’s needs. Primary treatment typically involves insulin therapy, which may require daily injections depending on the severity of the condition. Cat owners can learn to administer insulin, which is crucial as every feline’s insulin requirements may differ. Working closely with a veterinarian will help ensure that the correct dosages are administered at the right times. Alongside insulin therapy, dietary management plays a pivotal role in controlling glucose levels. Feeding a high-protein, low-carbohydrate diet can help regulate blood sugar fluctuations and support weight loss in overweight cats. Regular exercise is equally important in maintaining a healthy weight, promoting overall wellbeing, and supporting metabolic function. Additionally, monitoring blood sugar levels at home can empower pet owners to keep track of their cat’s condition effectively. Tech tools such as glucose monitors can help in this endeavor, making management easier. Overall, understanding the management plan will provide confidence in keeping diabetic cats healthy and happy.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is key in effectively managing diabetes in cats. Many cat owners use glucose monitoring devices to track glucose levels at home, allowing them to make data-driven adjustments to treatment as needed. Typically, blood sugar tests are carried out once or twice weekly, although frequency may increase as necessary. Understanding the optimal ranges for blood glucose is vital; levels that are too high or too low can be dangerous. Keeping a detailed log of glucose readings can help owners identify patterns and behaviors associated with fluctuations. Adjustments to diet or insulin dosages can then be made in consultation with a veterinarian based on these trends. Additionally, observing any behavioral changes such as lethargy or alterations in appetite should also be communicated to the vet. All these measures will provide a clearer picture of the cat’s health status. Early detection of complications is critical in preventing more severe health issues. Regular veterinary visits in tandem with home monitoring will enhance the overall management plan for diabetic cats.
Complications can arise from poorly managed diabetes in cats, emphasizing the need for ongoing care. Feline diabetic neuropathy is a common condition experienced by cats with prolonged hyperglycemia. This condition results in weakness and difficulty walking due to nerve damage. Observing changes in mobility or coordination should prompt immediate consultation with a veterinarian. Other potential complications include pancreatitis, dental disease, and urinary infections, all exacerbated by diabetes. Not only can these complications create additional challenges for the owner, but they can also significantly impact the cat’s quality of life. Managing weight and ensuring proper nutrition are crucial in mitigating these risks. Cats should receive regular dental check-ups to prevent oral diseases that can occur more frequently in diabetic felines. Veterinarians may recommend routine screenings and follow-ups to catch potential complications early. Promoting an active lifestyle will support overall health and reduce the chances of obesity and associated issues. Careful attention and proactive measures can allow diabetic cats to live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Conclusion on Diabetes Management
In conclusion, understanding and managing diabetes mellitus in cats is essential for their long-term health and wellbeing. Awareness of the causes, symptoms, and management techniques empowers pet owners to make informed decisions. Effective management involves a combination of insulin therapy, dietary adjustments, regular monitoring, and veterinary consultations. Early detection is crucial in preventing severe complications that could arise. Owners need to remain observant and responsive to behavioral and physical changes, as these can indicate the need for adjustments or interventions. By fostering an optimal environment promoting healthy habits, such as diet and exercise, many diabetic cats thrive in their homes. Working alongside veterinarians ensures that treatment plans are personalized and adjusted to meet changing needs over time. With dedication and commitment, a feline diagnosed with diabetes can live joyous, healthy life. By implementing the strategies discussed throughout this article, cat owners can build a supportive network for their pets, extending their lives while enhancing their quality of life significantly. Diabetes management in cats doesn’t just require medication; it involves holistic care that takes various aspects of a cat’s lifestyle into account.
Cats and their health demand attention from owners dedicated to providing the best possible care. The proactive approach described shows the level of commitment necessary to manage diabetes effectively. Regular check-ups with a veterinarian and adherence to a structured management plan can foster positive outcomes. Keeping up with educational materials regarding feline diabetes can enhance knowledge and ensure responsibility. Whether it’s understanding dietary needs, administering insulin, or observing symptoms, being informed lays the foundation for success. Also, consultations about any medications must be made with a veterinarian to ensure compatibility and efficacy. Owners should embrace a team approach, engaging with veterinary professionals and support groups related to feline diabetes. Sharing experiences with fellow cat owners can open up avenues for valuable advice and shared solutions to common challenges. Thus, widely accessible information can stimulate dialogue and support for those navigating this condition. In summary, creating an informed community provides confidence and assurance to tackle the challenges presented by feline diabetes. Overall, taking a holistic view of a diabetic cat’s health will contribute to its vitality and happiness.