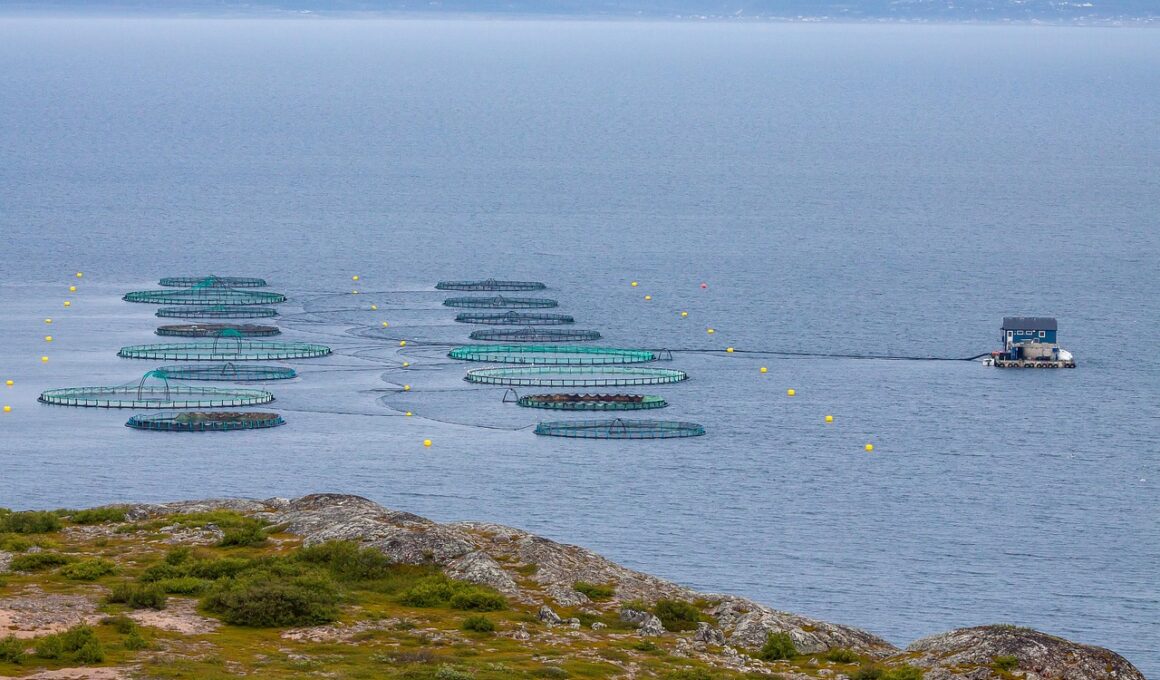
Sustainable Practices to Reduce Waste in Aquaculture
Aquaculture plays a vital role in meeting the growing global demand for seafood. Sustainable practices are increasingly essential for minimizing waste within this sector. Methods that focus on responsible fish farming techniques not only enhance productivity but also safeguard the environment. Among various strategies, adopting integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) is crucial. IMTA combines different species, where the waste from one species serves as a nutrient for another. This approach benefits various organisms, optimizing resource use efficiently. Additionally, adopting environmentally friendly feed ingredients significantly reduces waste. By employing fishmeal alternatives such as algae and insects, aquaculture can mitigate the reliance on traditional feed sources. These practices collectively contribute to a circular economy within the aquaculture sector. Enhanced waste management systems should also be prioritized. Implementing efficient biofilters can effectively reduce harmful nitrogenous waste, promoting healthier ecosystems. Implementing smart technologies for monitoring water quality further aids in waste reduction. Education and training for aquaculture practitioners on waste management strategies may also play a critical role in promoting sustainable practices. Overall, developing such strategies is paramount for a resilient aquaculture industry that benefits both society and the environment.
Continuing from sustainable practices, the significance of waste recycling cannot be overstated in aquaculture. Efficient recycling practices can drastically reduce waste generation in fish farms. One effective approach involves utilizing organic waste to produce biogas through anaerobic digestion. This process not only harnesses renewable energy but also minimizes methane emissions, addressing climate change concerns. Furthermore, valorizing waste by converting it into organic fertilizers can boost plant growth. This not only mitigates landfilling but also closes nutrient loops within the ecosystem. Implementing stringent regulations and best practices helps improve waste recycling initiatives across the industry. Cooperation between stakeholders and the government is crucial for the establishment of adequate infrastructure for composting organic waste. Additionally, creating awareness about the economic benefits of waste recycling in aquaculture can foster a positive attitude among fish farmers. Implementing initiatives such as community workshops and informational campaigns may enlighten practitioners on how to optimize waste recycling practices. These efforts lead to more sustainable fish farming systems while benefiting small-scale operations. Moreover, the development of technology and processes to safely process waste will bolster recycling activities in aquaculture. All of these factors combined enhance the industry’s overall sustainability and resilience.
The Role of Technology in Waste Reduction
Next, technology increasingly serves as a powerful ally in minimizing waste in aquaculture. Innovations in precision aquaculture allow for more efficient production methods that significantly reduce waste. By integrating advanced sensors and data analytics, farmers monitor water conditions, feed efficiency, and fish health closely. This enables timely interventions to prevent overfeeding and thus curtail waste generation. Additionally, automated feeding systems contribute to minimizing waste. By accurately dispensing feed according to real-time requirements, these systems ensure that fish receive the right amount of nourishment. IoT-based solutions further enhance monitoring and control throughout the farming process. This leads to optimized resource utilization, including water and feed management. Furthermore, advancements in genetic selection for fish species can result in strains that grow faster and require less feed, thereby reducing waste. Sustainable fish farming operations increasingly adopt these technological tools to embrace eco-friendly practices. Overall, the role of innovation is fundamental in reshaping aquaculture for improved waste management and resource efficiency. By fostering the growth of these technologies, stakeholders can create a sustainable future while addressing environmental concerns that accompany fish farming. Thus, investing in technology remains a priority for responsible aquaculture development.
Moreover, selecting suitable fish species plays a significant part in sustainable aquaculture practices. Choosing species that are resilient to local conditions, such as ones that require less feed, is critical for waste reduction. By focusing on these aquatic organisms, aquaculture can yield a higher benefit-to-cost ratio. For example, incorporating herbivorous species in the farming system encourages natural grazing behaviors, reducing reliance on commercially produced feeds. Implementing polyculture increases biodiversity in fish farms, allowing for a more balanced ecosystem. This method further creates symbiotic relationships, where one species thrives on waste from another. In addition, promoting local species strengthens the ecological resilience of aquaculture systems. Farmers can significantly reduce costs and waste by utilizing species better adapted to their environment. Supporting research in selective breeding strategies also enhances species performance and sustainability. Furthermore, community engagement helps build partnerships among local stakeholders and encourages collaboration for species selection. Education about the ecological impact of chosen fish can benefit the environment and profitability over time. Overall, focusing on selecting and promoting suitable fish species is a vital aspect of reducing waste in aquaculture, aligning industry goals with environmental sustainability.
Community Engagement and Education
Furthermore, engaging with local communities enhances sustainable aquaculture practices while reducing waste. Local stakeholders play a crucial role in creating a resilient aquaculture sector. Educating fish farmers on best practices can significantly improve waste handling and overall productivity. Governments and non-profit organizations can support this education by offering workshops, training programs, and resources that focus on waste reduction techniques. Highlighting successful case studies where waste management strategies were effectively implemented serves as an inspiration for practitioners. Through interactive activities, stakeholders gain practical experience and knowledge on minimizing waste in aquaculture. Community engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility toward sustainability goals. Initiatives supporting local aquaculture can also address food security and economic benefits. Providing extension services to fish farmers can facilitate access to tools and services that promote sustainable models. Collaboration among industry players ensures the exchange of ideas and practices is fruitful. Additionally, actively involving communities in ecological restoration contributes to the overall health of the local ecosystem. Social responsibility becomes embedded into aquaculture practices, making it a more sustainable industry. Thus, creating a strong community foundation is vital for implementing waste reduction strategies in aquaculture.
Lastly, regulatory frameworks are instrumental in supporting sustainable aquaculture practices aimed at waste reduction. Governments should form policies that endorse responsible waste management in aquaculture. Establishing and enforcing regulations would encourage compliance to best practices in waste handling. A cohesive framework can guide the industry toward sustainability by promoting the adoption of best practices. One effective approach would include setting specific waste reduction targets for fish farms. This could stimulate innovation and encourage the use of cleaner technologies and eco-efficient methods. Encouraging transparency and accountability in reporting waste generation further enhances responsible aquaculture operations. Stakeholders must work in partnership to develop guidelines that emphasize reducing impacts on the environment while providing steady business growth. Collaboration between various aquaculture sectors and regulatory authorities promotes an understanding of operational challenges. Additionally, integrating sustainability criteria into aquaculture funding programs would direct investments toward greener practices. Regulatory frameworks can play a pivotal role in fortifying the socio-economic viability of aquaculture while ensuring environmental preservation. Establishing clear measures ensures the aquaculture industry does not compromise environmental integrity in its growth journey. All these aspects collectively contribute to a sustainable and waste-reducing aquaculture sector.
Future Directions in Aquaculture Sustainability
As we consider future directions, collaboration and innovation will be essential for sustainable aquaculture. Stakeholders must work together to create scalable solutions that address waste reduction challenges. Embracing research and development efforts focused on advanced, sustainable technologies will empower farmers to minimize waste effectively. Additionally, cross-industry cooperation may bolster effective practices, sharing knowledge across sectors, such as agriculture and fisheries. This collaboration may spark new ideas, fostering creativity and innovation in waste management strategies. Transparency and traceability are also crucial in the journey towards sustainability. Stakeholders should prioritize implementing certification programs that endorse responsible aquaculture practices. By ensuring that fish products adhere to strict sustainability criteria, consumers can make informed choices. Investing in learning initiatives to support farmers on these subjects adds further value. Communities and academic institutions can facilitate collaborative partnerships that focus on conduct and research, ultimately creating innovative solutions for sustainable aquaculture. Promoting responsible consumption habits can also drive demand for sustainably farmed seafood. This alliance exerts pressure on producers to adopt eco-friendly practices. Overall, these collaborative and innovative approaches are essential for charting a sustainable future for aquaculture and minimizing waste effectively.
In conclusion, sustainable practices to reduce waste in aquaculture are critical for environmental health and food security. By implementing integrated multi-trophic aquaculture, innovative technologies, proper species selection, and promoting community engagement, the industry can foster responsible practices. Waste recycling through biogas production and organic fertilizers plays an essential role in minimizing negative impacts. Establishing regulatory frameworks that support sustainability ensures the commitment of all stakeholders. Education and training programs for practitioners further enhance waste management efforts. These initiatives must acknowledge the importance of collaboration and innovation among industry members to pioneer effective waste management. Ultimately, encouraging consumer awareness and responsible practices is vital for market demand. A collective movement is necessary to drive meaningful change. While the industry faces challenges, the integration of sustainable practices presents an opportunity for positive transformation. By continuing to innovate and engage with communities, aquaculture can contribute to healthier ecosystems and sustainable food systems. As aquaculture evolves, it remains critical to align industry practices with sustainable development goals. The journey towards minimizing waste in aquaculture is a collaborative effort requiring collective commitment from all stakeholders.