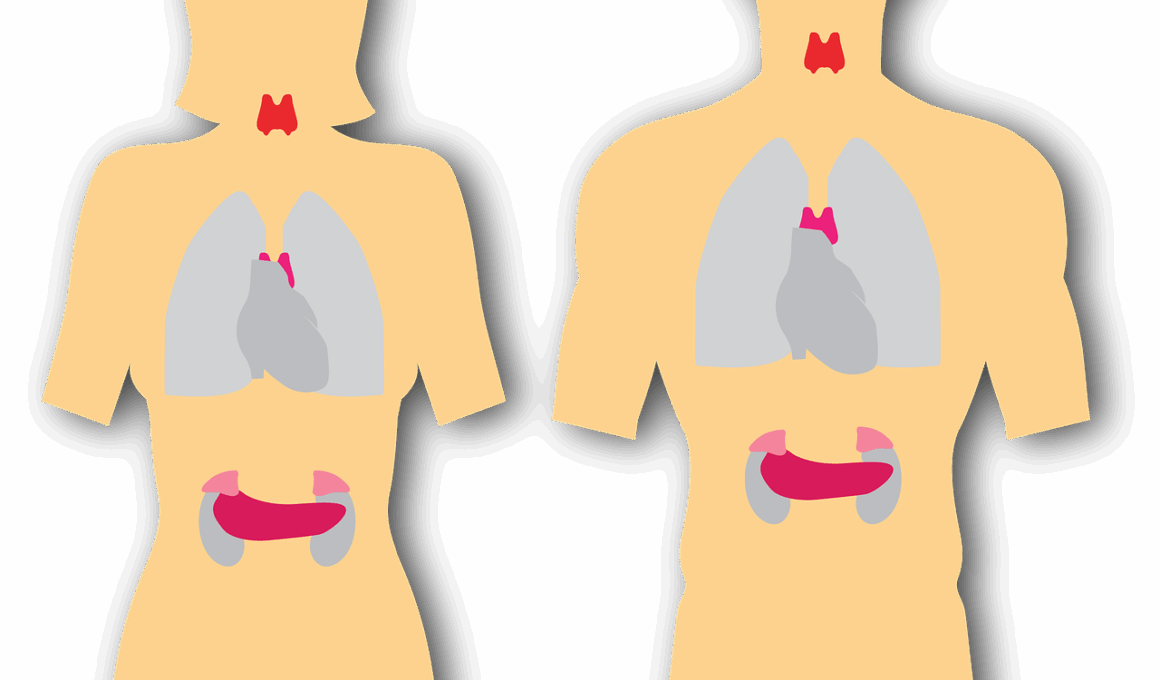Animal Endocrine System Disorders and Diseases
The endocrine system is essential in regulating various bodily functions through hormonal secretions in animals. Disorders of this system can range from mild to life-threatening. Common endocrine disorders include diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, and Cushing’s disease. Diabetes mellitus leads to inadequate insulin production or insulin resistance, resulting in high blood glucose levels. On the other hand, hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive hormones, causing symptoms such as weight loss, increased appetite, and hyperactivity. Cushing’s disease results from excessive cortisol production, leading to severe metabolic imbalances. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing these conditions effectively.
Another prevalent hormonal disorder is hypothyroidism, which is characterized by insufficient thyroid hormone production. Symptoms often include lethargy, weight gain, and a poor coat condition. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure hormone levels. Treatment usually consists of thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Additionally, some endocrine disorders may stem from tumors, such as adrenal tumors causing excessive hormone secretion. These conditions can severely impact an animal’s quality of life without proper intervention. Routine veterinary check-ups are vital for early detection. If left untreated, these disorders may lead to significant complications affecting the animal’s health and well-being.
The adrenal glands are also susceptible to various disorders, including Addison’s disease. This condition results in insufficient production of hormones like cortisol and aldosterone. Symptoms include severe fatigue, vomiting, and low blood sugar levels. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests and imaging to assess adrenal gland function. The treatment generally requires hormone replacement therapy. Furthermore, hormonal imbalances may affect reproductive health in animals, potentially leading to conditions such as infertility or irregular cycles. Understanding these disorders can help pet owners recognize signs and seek veterinary care for their animals.
Endocrine Disorders in Different Species
Endocrine disorders can manifest differently across various animal species. For instance, canines often experience diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism, while felines frequently suffer from hyperthyroidism. Treatment approaches can vary based on the specific species affected. In dogs, insulin therapy is commonly used to manage diabetes, while felines may require radioactive iodine treatment for hyperthyroidism. Additionally, horses can be at risk for Cushing’s disease, which affects their overall health, including coat condition and susceptibility to infections. Understanding species-specific disorders aids in accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
In addition to common hormonal issues, some breeds may be more prone to specific endocrine disorders. For example, Doberman pinschers and golden retrievers are particularly susceptible to hypothyroidism. Recognizing breed predispositions can assist veterinarians in early screenings and interventions. Conversely, some animals may develop secondary endocrine disorders due to other health complications. For instance, chronic kidney disease can also impact endocrine function, leading to further challenges in management. Comprehensive assessments help identify underlying factors for more effective treatment strategies, ensuring holistic health care for the animal.
Diet and lifestyle significantly influence the endocrine system’s health in animals. Obesity, for instance, can exacerbate hormonal disorders, particularly in dogs and cats. Keeping pets at a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise is crucial. Additionally, certain environmental factors, such as exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals, have been linked to increased incidence of disorders. Pet owners should be aware of these risks and strive to create safe, chemical-free environments. Ensuring pets maintain a well-rounded diet is vital to reducing the risk of developing endocrine diseases.
Latest Research and Advances in Treatment
Recent research has shown promising advances in the treatment of endocrine disorders in animals. Studies exploring new medications and therapies aim to enhance hormone regulation and improve the quality of life for affected animals. For example, insulin pumps are being evaluated for managing diabetes more effectively. Additionally, researchers are investigating the genetic factors contributing to endocrine disorders, paving the way for targeted therapies in the future. Staying informed about these advancements enables veterinarians to provide the best possible care and treatment options. Public awareness of these issues can help dispel myths regarding endocrine diseases and encourages owners to seek timely veterinary support.
Preventative care remains the most effective strategy against endocrine disorders. Regular veterinary examinations, combined with blood tests, can detect early signs of hormone imbalances. Pet owners should monitor their animals for any abrupt changes in behavior, appetite, or energy levels. Being proactive about health assessment can lead to timely interventions, potentially preventing the progression of endocrine diseases. Furthermore, educating pet owners about proper nutrition, exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial aspects of preventive care. Together, these initiatives can significantly improve the overall health and longevity of pets.