The Role of Plant Matter in the Diets of Herbivorous Prey Species
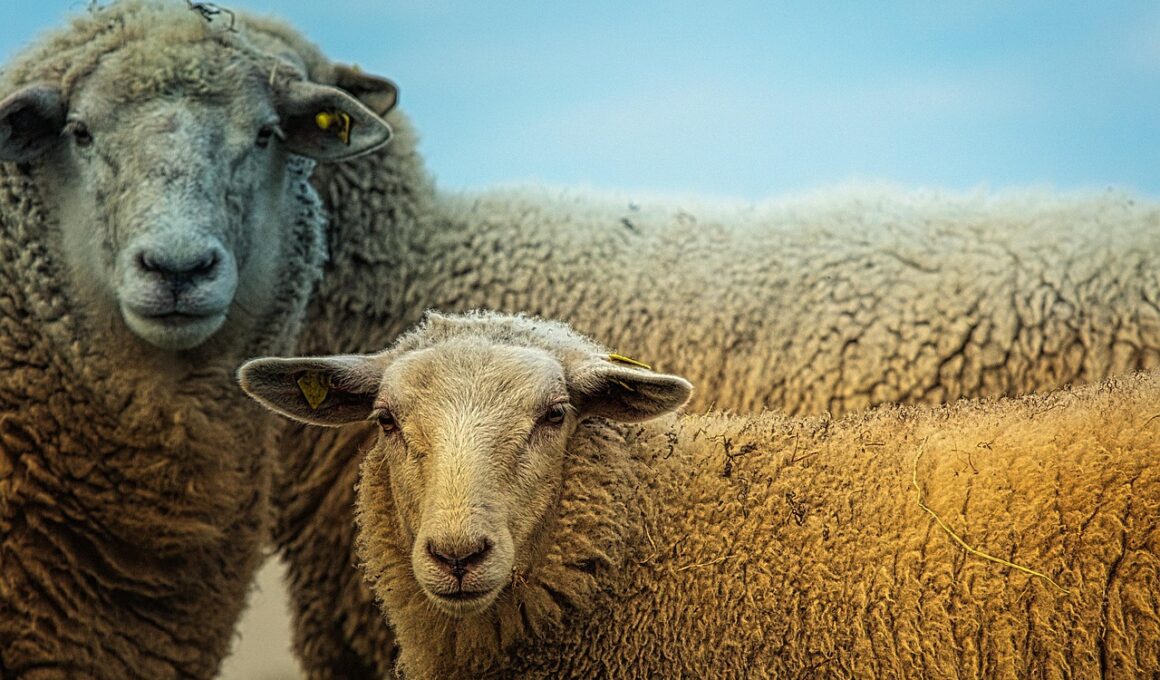
Herbivorous prey species constitute a significant part of various ecosystems, relying heavily on plant matter for their nutritional needs. These species, such as deer, rabbits, and elephants, have evolved specialized physical and behavioral adaptations that enable efficient extraction of nutrients from their plant-based diet. The primary consumption source includes leaves, stems, roots, and fruits, presenting diverse opportunities for nutrient acquisition. The digestibility of plant matter varies widely due to factors such as plant fiber composition and secondary metabolites present within different species. Additionally, herbivores often develop extensive social structures, participating in group foraging behavior which allows them to maximize dietary intake while minimizing predation risk. A consistent understanding of the nutritional needs and plant preferences of these herbivores can inform conservation strategies. Various ecological studies highlight the balance these species maintain within their environments, influencing plant community dynamics. Understanding the intricate relationships between herbivores and their food sources provides insights into ecosystem health. Ultimately, herbivore diets showcase the complexity of interdependent relationships that comprise food webs in natural habitats. Recognizing their role is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and sustainable management of ecosystems.
The morphology of herbivorous prey species plays a pivotal role in their ability to process plant matter effectively. These adaptations extend from dental structure to digestive systems, enabling these species to break down fibrous plant material efficiently. For example, ruminants like cows and sheep possess specialized stomach compartments that allow for fermentation, enhancing nutrient extraction from tough plant fibers. This process not only maximizes nutrient absorption but also offers advantages during periods of food scarcity. Many herbivores, including those that inhabit arid environments, have physical adaptations that complement their dietary choices. These adaptations ensure that they can exploit various plant resources efficiently while facing environmental challenges. Furthermore, behaviors such as selective feeding allow herbivorous prey to choose nutrient-dense food sources, further optimizing their nutritional intake. Recent research indicates that the timing and frequency of feeding can significantly impact energy acquisition and reproductive success in these species. As prey animals navigate their environments, understanding the ecological implications of these feeding habits is vital to preserving their populations. This information can aid in developing better management practices aimed at maintaining specific prey species and their habitats.
Impact of Seasonality on Plant Consumption
Seasonal changes dramatically influence the availability and nutritional quality of plant matter consumed by herbivorous prey species. During spring and summer, the abundance of fresh, nutrient-rich vegetation presents optimal foraging opportunities. In contrast, winter often brings a marked decline in the diversity and accessibility of food sources. Many herbivorous species adjust their dietary patterns accordingly, seeking alternative food sources such as bark, roots, or stored energy reserves. These adaptations reflect a crucial survival strategy, enabling herbivorous prey to sustain their energy levels during harsh conditions. The growth cycles of plants dictate the availability of vital nutrients—key vitamins and minerals are often less prevalent in winter months. Moreover, environmental factors, such as drought or excessive rainfall, can further exacerbate nutritional shortages during certain seasons. Understanding these fluctuations provides vital insights into herbivore behavior and overall ecosystem health. Conservation efforts must incorporate these seasonal dynamics to ensure that herbivorous prey have adequate resources throughout the year. Addressing these considerations is essential for promoting long-term survival and reproductive success in various herbivore populations across diverse ecological landscapes.
In addition to seasonality, herbivorous prey species often exhibit different feeding strategies based on habitat availability. The diversity of ecosystems provides various plant species, each influencing the dietary habits of these animals. Grasslands, forests, and wetlands present distinctive plant communities that contribute to the overall diet. For instance, the availability of legumes in grasslands offers crucial proteins that enhance the nutritional intake of herbivores. Meanwhile, forest habitats often provide a mix of leaves and fruits that support different dietary needs. This ecological niche variation plays a fundamental role in shaping herbivore populations and their interactions with plant communities. Competition among herbivorous species for limited food sources can also drive adaptations in feeding behavior and foraging efficiency. Understanding habitat preferences and the subsequent impact on herbivore diets sheds light on biodiversity conservation efforts. As ecosystems face increasing pressures from climate change and human activities, recognizing how habitat dynamics influence herbivore diets becomes crucial. Implementing informed management strategies that consider the specific dietary needs of various prey species can ultimately foster healthier ecosystems, balancing both plant and herbivore populations in a sustainable manner.
Role of Herbivores in Ecosystem Dynamics
Herbivorous prey species significantly influence ecosystem function, serving as critical moderators of plant community dynamics. By consuming various plant species, these herbivores shape vegetation structure and composition, facilitating nutrient cycling and habitat maintenance. Their feeding habits can promote biodiversity by enabling certain plants to thrive while controlling the dominance of others. For example, grazers can prevent overgrowth, allowing diverse plant communities to flourish. This ultimately supports a wide range of other organisms, creating a balanced food web. Additionally, herbivores play an integral role in seed dispersal, actively contributing to plant reproduction and contributing to genetic diversity. Moreover, herbivore populations can influence soil health due to their grazing behavior, enhancing nutrient availability for plant growth. In turn, these positive effects on vegetation and soil foster habitat suitability for countless species. The interconnectedness of herbivores within their ecosystems demonstrates the importance of maintaining healthy herbivore populations for overall biodiversity. Conservation practices must take into account the essential roles that herbivorous prey play in sustaining ecosystems. It is necessary to promote measures that ensure their survival amidst environmental pressures and challenges in modern landscapes.
Furthermore, the relationship between herbivorous prey and their predators highlights an essential aspect of ecosystem balance. Herbivores occupy a crucial position in food webs, serving as prey for numerous carnivorous species. This predation pressure influences herbivore foraging behavior, contributing to their dietary choices and overall health. When herbivore populations are abundant, they can sustain larger predator populations, which in turn impacts grazing pressure on plant communities. Conversely, when predator populations decline, herbivore numbers can increase disproportionately, leading to overgrazing and potential degradation of vegetation. This cycle underscores the need for balanced predator-prey dynamics to maintain healthy ecosystems. Recent studies indicate that managing predator populations can have significant implications for herbivore diets and behaviors, significantly affecting ecological integrity. Conservation practitioners face the challenge of developing strategies that support not only herbivore populations but also their associated predators. Long-term ecological monitoring of these dynamics will provide valuable insights into the complex interactions that define ecosystems. Sustainable management of both herbivores and predators is critical for ensuring the health of diverse habitats and safeguarding the interconnected species within them.
Conclusion: Implications for Conservation
The importance of understanding herbivorous diets extends beyond mere ecological interest; it has direct implications for conservation strategies aimed at preserving biodiversity. Effective management requires recognizing the intricate relationships between herbivores and their preferred plant sources, as well as the consequences of seasonal changes and habitat variations. Conservation efforts should focus on safeguarding specific food plants critical to herbivore survival while considering broader environmental factors influencing these dynamics. Collaborations between ecologists and conservation practitioners can enhance strategies that promote ecosystem health by integrating knowledge of herbivorous dietary needs. It is vital to assess how changes in land use and climate may alter plant communities, affecting herbivore populations. Therefore, adaptive management strategies supported by rigorous ecological research remain essential for protecting herbivorous prey species and the habitats they inhabit. Embedding these insights into management practices can lead to more resilient ecosystems, capable of sustaining diverse animal populations. A balanced approach focused on preserving both plant communities and herbivores will undoubtedly enhance ecosystem health. As our understanding of these interactions deepens, the path toward effective conservation measures becomes clearer, ultimately benefiting wildlife and habitats alike.
In summary, the role of plant matter in the diets of herbivorous prey species is multifaceted and critical for ecosystem stability. These species have evolved unique adaptations and strategies that enhance their ability to thrive on plant-based diets. Seasonal shifts, habitat variances, and ecological interactions all contribute significantly to shaping herbivore feeding habits. Recognizing these factors is crucial for developing informed conservation practices that look to maintain biodiversity. The relationships between herbivores, their predators, and the plant communities they rely upon illustrate the interconnectedness of ecological systems. As we face increasing environmental challenges, prioritizing the conservation of these intricate relationships becomes ever more critical. Steps taken to protect herbivorous prey can have far-reaching effects on broader ecosystem health, ultimately ensuring that diverse flora and fauna continue to flourish. Moving forward, conservation strategies should incorporate comprehensive understanding of herbivorous needs, seasonal considerations, and habitat dynamics. By fostering a balanced ecosystem approach, we can support the survival of herbivorous prey and the various species that depend on them. Thus, the role of plant matter in these diets remains pivotal, underscoring its significance within ecological networks.