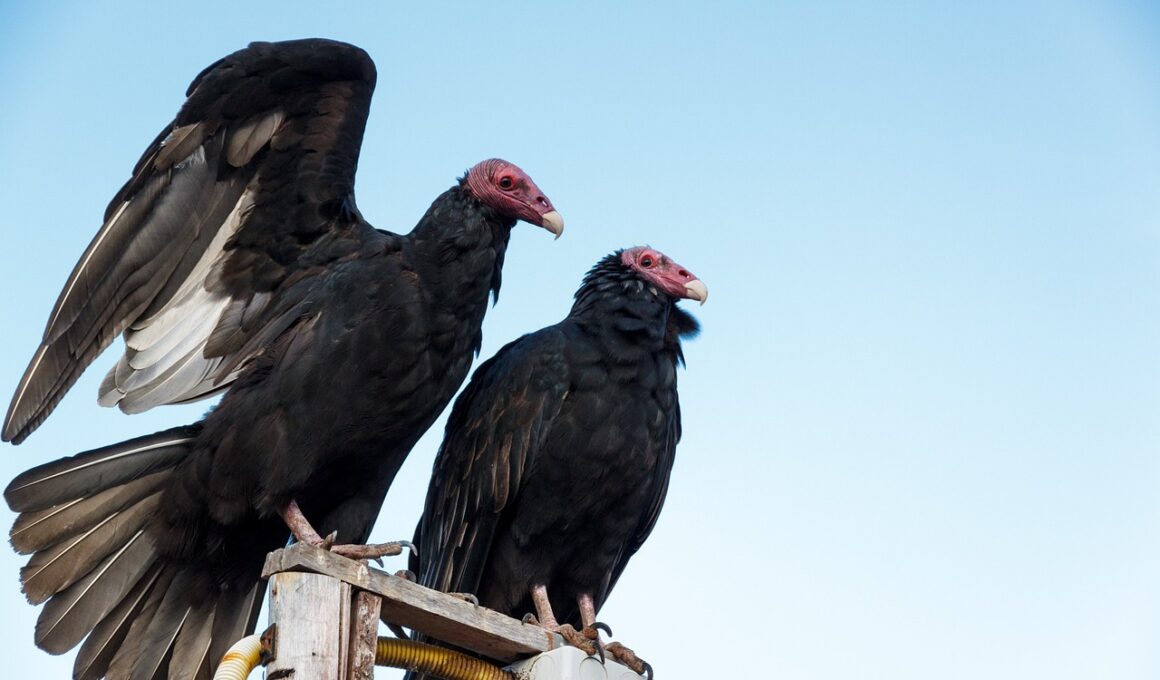
Desert Scavengers: Nature’s Cleanup Crew
Desert scavengers play an essential role in maintaining the ecosystem of arid regions. These animals are specially adapted to survive in harsh conditions where food can be scarce. They thrive on carrion, the decaying remains of dead animals, and help control the spread of diseases. Scavengers reduce the risk of contamination by consuming organic remains, thus promoting a healthier habitat. Among the most recognized scavengers are vultures, hyenas, and various insects. Vultures, with their incredible eyesight, can spot carcasses from great distances. Similarly, hyenas are not solely hunters; they scavenge extensively and utilize their strong jaws to consume tougher materials. Insects, like beetles, also contribute significantly to the decomposition process. They break down organic matter, enriching the soil and ensuring that nutrients are recycled within the ecosystem. Their actions promote biodiversity, as they support various species that rely on cleaner environments. By removing waste, desert scavengers assist in sustaining life forms that would otherwise struggle in dry climates. Protection and conservation of these scavengers are crucial for desert ecosystems.
The Importance of Scavengers
Scavengers are vital for the ecological balance in desert environments. They participate in nutrient cycling, which facilitates plant growth and supports the overall food web. Without scavengers, ecosystems would encounter numerous challenges leading to environmental degradation. Decomposed remains are an excellent source of nutrients for the soil, promoting healthy plant life. Furthermore, by consuming carrion, they minimize the potential for disease outbreaks. Dead animals can harbor pathogens; thus, scavengers act as natural sanitation workers that mitigate health risks. Additionally, their feeding habits encourage biodiversity, as many other species rely on healthy ecosystems for survival. Many smaller creatures benefit when scavengers consume large carcasses and leave behind scraps. Such actions provide additional food sources for other wildlife, creating a thriving community of interdependent species. Furthermore, research indicates that maintaining scavenger populations directly correlates with vibrant ecosystems. This relationship signifies the importance of preserving not just the scavengers themselves but their habitats too. Communities must actively engage in conservation efforts that safeguard these critical species and their environments to ensure ecological health and biodiversity.
In arid desert climates, scavengers display remarkable adaptations that aid in their survival. For instance, many scavengers possess keen eyesight and acute senses that allow them to locate carrion over vast distances. Vultures, primarily scavengers, can soar high above the terrain, spotting potential meals without using excessive energy. On the ground, scavenging mammals like coyotes and jackals possess excellent olfactory capabilities, enabling them to detect food buried beneath layers of sand or vegetation. Their physical traits, such as strong jaws and resilient stomachs, help in the intake and digestion of tougher materials, showcasing their prowess as scavengers. However, these adaptations also make them susceptible to environmental changes that impact food availability. Climate change threatens their habitats by altering the distribution of prey and reducing available carrion. Excessive hunting can also jeopardize scavenger populations. To mitigate these threats, conservationists promote habitat protection and sustainable practices that benefit both scavengers and their ecosystems. Maintaining a balance is crucial, not just for these scavengers but for the entire desert community relying on them for survival, further stressing their ecological significance.
Threats Faced by Desert Scavengers
Desert scavengers face myriad threats that jeopardize their populations and the ecosystems they support. Habitat destruction, primarily due to human activities, significantly affects their survival. Urbanization and agriculture encroach upon their natural territories, reducing available resources. Additionally, climate change presents a serious challenge by altering prey distributions and food availability. Food scarcity forces scavengers to compete, leading to increased mortality rates. Hunting and poaching further exacerbate their plight, as some scavengers are targeted for elimination out of fear or misunderstanding. For example, vultures have suffered drastic population declines due to poison exposure from carcasses intentionally treated with toxins to eliminate other wildlife. Educating communities about the importance of these species can foster support for their protection. Increased awareness can lead to conservation initiatives focused on preserving habitats, enforcing legal protections, and developing sustainable practices. Conservation organizations often engage local populations to promote coexistence and appreciation for the invaluable role scavengers play in desert ecosystems. By addressing these threats through dedicated efforts, we can contribute to the resilience of scavenger populations and the health of arid environments.
Conservation strategies for desert scavengers focus on habitat preservation and public advocacy to raise awareness of their significance. This can include establishing protected areas that shield critical habitats from development or agricultural activities. Collaborating with communities helps to create buffer zones around natural reserves, ensuring that scavengers have consistent access to food. Furthermore, NGOs play an essential role in facilitating research on the behaviors and needs of scavengers. Such studies inform policies targeting preservation and protection. Education initiatives serve a dual purpose: informing the public about the ecological benefits scavengers offer while fostering a sense of responsibility to protect local wildlife. Engaging communities can lead to successful conservation programs built on local knowledge and traditions. Another crucial aspect of these strategies is monitoring scavenger populations and the environmental changes they endure. By tracking their numbers and health, researchers can identify trends and take action if certain populations begin to decline significantly. Species recovery programs focus on breeding and reintroducing scarce scavenger species back into their natural habitats, promoting genetic diversity and stability within ecosystems.
Successful Conservation Efforts
Examples of successful conservation efforts demonstrate how immediate action can positively impact desert scavenger populations. Reintroduction programs for vultures in various regions have shown remarkable results in rebuilding their numbers. These initiatives often include educating local communities and implementing laws to protect scavengers from poisoning and habitat loss. Furthermore, collaborations between conservation organizations and government bodies have resulted in increased funding for research and habitat restoration projects. Rehabilitation centers for injured scavengers provide necessary medical care and support, enabling their return to the wild. Several studies also highlight how holistic approaches addressing the interconnected nature of ecosystems are essential. These efforts coordinate conservation work across multiple species, recognizing the role that scavengers play in supporting their habitats. International cooperation is also increasing; countries share information and resources to develop effective strategies for protecting migratory scavengers. Efforts to reduce human-induced threats, such as education about the impacts of poisoning and habitat encroachment, are also critical. Public campaigns work towards changing perceptions about scavengers, emphasizing their ecological roles, and garnering support for long-term conservation goals to secure their futures.
The future of desert scavengers hinges on continued awareness and proactive conservation strategies tailored to their specific needs. As climate change impacts ecosystems worldwide, it is essential to implement adaptive management practices that consider these challenges. Research will play a pivotal role in understanding how changing conditions will affect scavenger populations. Global initiatives focused on mitigating climate change will be crucial in ensuring that desert ecosystems remain viable for scavengers and the species they support. Community engagement and education must remain at the forefront, encouraging individuals to appreciate and protect desert scavengers and their habitats. Efforts to promote cohabitation with scavengers can enhance their survival, decreasing human-wildlife conflicts. Collaboration among stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and local communities, fosters a collective commitment to shared environmental goals. Developing sustainable agricultural practices can also help safeguard the interests of scavengers while supporting communities dependent on these lands. Ultimately, an informed society must champion scavenger conservation by understanding their vital importance to the ecosystem. Only through dedicated efforts and collaboration can we ensure that these unique and essential creatures continue to thrive in the deserts of the future.
Desert scavengers play an essential role in maintaining the ecosystem of arid regions. These animals are specially adapted to survive in harsh conditions where food can be scarce. They thrive on carrion, the decaying remains of dead animals, and help control the spread of diseases. Scavengers reduce the risk of contamination by consuming organic remains, thus promoting a healthier habitat. Among the most recognized scavengers are vultures, hyenas, and various insects. Vultures, with their incredible eyesight, can spot carcasses from great distances. Similarly, hyenas are not solely hunters; they scavenge extensively and utilize their strong jaws to consume tougher materials. Insects, like beetles, also contribute significantly to the decomposition process. They break down organic matter, enriching the soil and ensuring that nutrients are recycled within the ecosystem. Their actions promote biodiversity, as they support various species that rely on cleaner environments. By removing waste, desert scavengers assist in sustaining life forms that would otherwise struggle in dry climates. Protection and conservation of these scavengers are crucial for desert ecosystems.