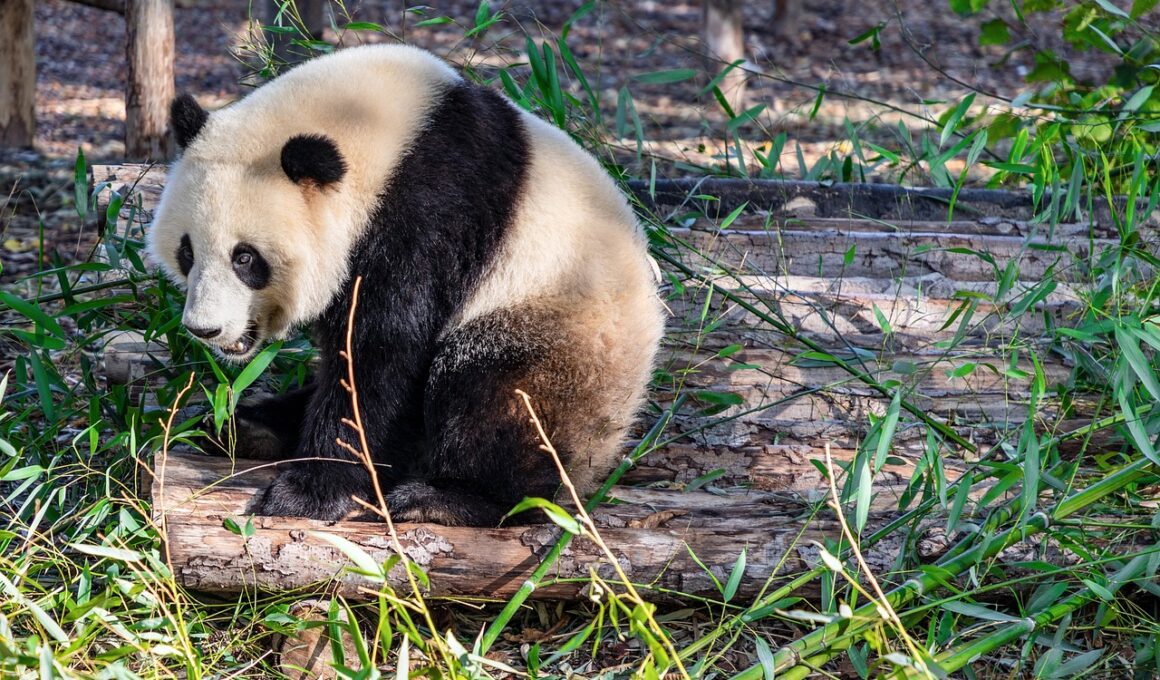
Giant Panda Life Cycle: From Birth to Adulthood
The Giant Panda, an iconic symbol of wildlife conservation, is native to the mountainous areas of China. Born very small and helpless, cubs weigh about 100 to 200 grams at birth. Within their first months, they rely exclusively on their mother’s milk, developing rapidly. During this time, their mother’s nurturing is critical. Female pandas prepare special nests for giving birth, often choosing hollows in trees or sheltered areas. These care routines remain consistent as their cubs grow. At around six months, the cubs begin to emerge from their nests, becoming more curious about their surroundings. Their distinctive black-and-white markings offer camouflage among the rocky landscapes and grassy terrains of their habitat. As they approach one year of age, pandas start to nibble on bamboo, slowly transitioning to solid food. To survive, they need vast forests filled with bamboo, which constitutes over 99% of their diet. With natural predators such as leopards and the encroachment of human activity, panda cubs face significant challenges throughout their early life stages. The conservation efforts placed upon them have been crucial in increasing their population, yet various threats still impact their survival.
Early Development and Milestones
During the initial months, panda cubs experience extraordinary growth, marked by many milestones. By the time they reach two months, they begin to open their eyes. This remarkable change promotes further exploration of their surroundings. With the guidance of their mothers, these young pandas develop vital skills crucial for survival. They observe and mimic their mothers’ actions, learning to climb trees—a skill essential for escaping potential dangers. At around three months old, the cubs grow more mobile, roaming areas near their nests while remaining under their mothers’ watchful eyes. Mothers generally raise one or two cubs at a time but often can only nurture one due to limited resources. Each cub forms a particular bond with its mother, relying on her protection and teaching. As they grow, playful behaviors take center stage; cubs frequently engage in mock fighting, developing social skills essential for adult life. These interactions foster a bond that ensures their chances of survival. As they reach their first birthday, they shift from maternal dependence towards becoming independent foragers, honing vital instincts, and preparing for the adult challenges that await them. This transition is essential for their future well-being.
The transition from cubs to adulthood takes several years, marked by notable behavioral changes typical to Giant Pandas. As they reach about 18 months, these pandas become increasingly independent, often venturing away from their mother. During this exploration phase, they learn to navigate their environment, discovering food sources and waterfalls integral to their habitat. Female young pandas can stay with their mothers until they are about 2-3 years old, while males often leave sooner. This period of independence is critical for their development, providing the opportunity to fully engage in local ecosystems. Giant Pandas are known for their low reproductive rate, as females are only fertile once a year, typically for 2-3 days. This biological characteristic adds a layer of complexity to their reproductive success. As they mature, finding a mate becomes essential, and older pandas exhibit unique courting behaviors marked by vocalizations and specific postures. Their interactions are often playful before becoming serious, showcasing the depth of emotional connections among the species. Understanding these social dynamics is crucial for preserving panda populations and ensuring their continued existence for future generations.
Diversity in Habitats
The Giant Panda’s habitat varies significantly according to different environmental conditions across their range. Primarily found in the mountainous regions of southwestern China, they thrive in moist, temperate forests with abundant bamboo. This habitat is essential, as bamboo supplies approximately 99% of their diet. However, Giant Pandas do not simply exist in one particular environment. They can adapt well to diverse altitudes, from approximately 1,200 to 3,400 meters above sea level. Within these forests, bamboo species also vary, comprising around 30 types that provide ample food sources. The availability of bamboo directly influences their population density, making habitat conservation efforts vital. In recent years, habitat loss due to urban development, fragmentation, and climate change poses a notable threat to these gentle giants. Ensuring a connected landscape for panda populations is crucial for their genetic diversity and survival. By maintaining corridors between isolated habitats, conservationists aim to mitigate these threats and promote healthy breeding. In combination with breeding programs, habitat restoration initiatives have also gained traction, providing opportunities for Giant Pandas to thrive, as they are part of complex ecosystems that require attention and protection.
Reproductive Strategies
Reproduction among Giant Pandas is characterized by both challenges and unique strategies that support species survival. As mentioned earlier, female pandas have a short breeding period that lasts only for 2-3 days each year; this temporal limitation makes finding a mate important yet challenging. Male pandas exhibit unique behaviors, such as vocalization and scent-marking, to attract females and establish territorial boundaries. These mating rituals can be quite elaborate, showcasing the pandas’ impressive agility and strength. Following successful mating, the gestation period lasts about 95 to 160 days. Females may give birth to one or two cubs, but often more will only survive if resources are plentiful. In many observations, mothers prioritize raising the stronger or healthier cub, leaving the other to perish. This natural selection ensures the most likely candidate thrives and reaches maturity. Additionally, female pandas demonstrate an incredibly strong maternal instinct, nurturing their young with unwavering dedication. This species has evolved particularly favorable traits to maximize the chances of cub survival, solidifying its place in the ecology and making awareness of it vital as conservation efforts continue to progress.
Giant Pandas play a critical role in maintaining their ecosystem, serving as an umbrella species that promotes overall biodiversity within their habitats. As they consume large quantities of bamboo, they influence the growth patterns of this key vegetation. This relationship between pandas and bamboo is both complex and symbiotic, contributing to the health of their forest environments. Additionally, their foraging habits assist in the dispersal of seeds within their territories, fostering the growth of various plant species. This role emphasizes why protecting panda habitats is essential—not just for their preservation but for sustaining the entire ecosystem. Without sufficient panda populations, these environments could face significant shifts that affect various flora and fauna. Conservation initiatives, including habitat restoration and the establishment of panda reserves, strive to maintain balance and ensure the health of these delicate ecosystems. Moreover, educating the public about the importance of Giant Pandas in their environment can bolster support for both conservation and restoration efforts. Engaging local communities in conservation work, tourism, and awareness can amplify these efforts, significantly impacting the future of the giant pandas and their vital ecosystems.
Conclusion and Conservation Efforts
The survival of Giant Pandas hinges upon continuous efforts to address the challenges they face. Conservationists and researchers have worked tirelessly to implement strategies that not only focus on their immediate survival but also aim to restore and enhance their habitats. Vast initiatives involving habitat preservation, fostering genetic diversity through captive breeding, and creating wildlife corridors to connect isolated populations are fundamental to these solutions. Public engagement through educational campaigns highlights the importance of protecting this species and its environment, building a grassroots level of support. By creating a collective global effort to safeguard ecosystems worldwide, we can ensure that future generations will be able to appreciate the beauty and significance of these gentle giants. The integration of technology with traditional conservation methods also shows promise in monitoring panda populations more effectively. Continued funding and scientific research contribute to developing new methodologies aimed at mitigating human impacts on panda habitats. Only through collaboration and dedicated efforts can we ultimately promote a harmonious coexistence between Giant Pandas and their surroundings, ensuring these remarkable creatures thrive along with the diverse ecosystems they inhabit. Immediate action is necessary to ensure their bright future.
For an enriching visual understanding of the Giant Panda’s life cycle, consider exploring wildlife photography or documentaries that showcase their habitats, behaviors, and nurturing practices. Such resources can significantly enhance awareness about conservation, inspiring individuals to support these efforts actively. Websites dedicated to wildlife conservation and local panda centers often offer valuable insights and opportunities for involvement. By engaging with communities that foster panda conservation, you can contribute to their sustainability. Each step taken toward understanding and preserving the habitat of Giant Pandas impacts not only the species, but biodiversity in those ecosystems as a whole. Additionally, opportunities for volunteering or donations to organizations focused on conservation often arise. These contributions help fund scientific research and habitat restoration programs essential for panda longevity. Participating in citizen science projects can also provide individuals with hands-on experience while fostering a sense of accountability to nature. Therefore, consider utilizing the various resources available to become an advocate for Giant Pandas, ensuring a safe and sustainable environment for future generations. As awareness continues to grow, so does the potential to generate meaningful change in wildlife conservation efforts.