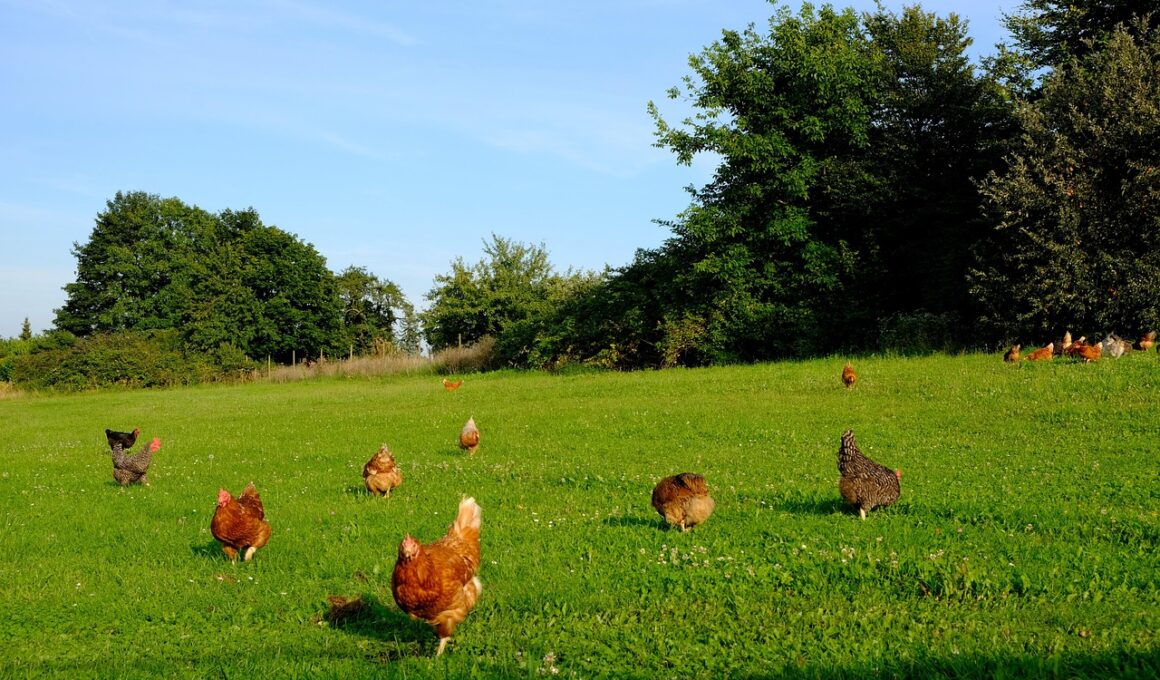
The Science Behind Free-Range and Organic Animal Feeding
Animal nutrition plays a vital role in ensuring the well-being and productivity of livestock. Free-range and organic feeding methods emphasize natural growth and holistic approaches, which can significantly influence animal health. By allowing animals access to outdoor space, they experience enrichment through fresh air and sunlight, contributing to their physical and mental well-being. Nutritionally, free-range systems often provide livestock with a varied diet comprised of grasses, insects, and natural forage. Animals raised under these conditions usually exhibit fewer health issues, and their products, like meat and eggs, are considered healthier. Moreover, the nutritional value differs due to the animals’ diverse diets compared to those raised in conventional systems. Organic feeding prohibits antibiotics and synthetic additives, promoting animal health positively. Additionally, it adheres to strict regulations regarding feed and supplements, ensuring a balanced nutrient profile. This leads to better digestive health and higher quality protein sources. Consumers increasingly seek out free-range and organic products, valuing animal welfare and sustainable practices as part of their purchasing decisions. The benefits of these methods extend not only to animals but also to ecosystems benefiting from regenerative practices.
Health Benefits of Free-Range Nutrition
The health benefits gained from free-range and organic nutrition are notable for both the animal and consumer. Animals that are permitted to forage outdoors tend to have more active lifestyles. This activity allows for the development of stronger muscles and better overall health. Additionally, free-range diets are typically richer in omega-3 fatty acids as a result of grazing on grass. This also means livestock can attain a healthier balance of fats. From a consumer perspective, products derived from free-range or organic systems are generally healthier. The presence of higher nutrient levels, especially in eggs and meats, enhances the quality of these products. For instance, organic eggs often boast more vitamin D and have lower cholesterol levels. Moreover, the absence of synthetic additives in organic feed ensures a cleaner food source for consumers, lowering the risks associated with chemical residues. Growth hormones are also prohibited, reflecting a commitment to maintaining both animal health and consumer safety. Additionally, the ethical treatment of animals amplifies the positive sentiment among consumers who prioritize animal welfare in their purchasing choices.
Environmental sustainability is another key advantage associated with free-range and organic animal feeding practices. These methods often promote biodiversity, maintaining healthier ecosystems. Livestock raised in free-range environments are more likely to thrive without the need for excessive antibiotics or chemical treatments. This helps to reduce the chances of developing antibiotic resistance among bacteria, a growing public health concern. Additionally, organic farms tend to implement sustainable practices such as crop rotation and reduced chemical use, improving soil health and reducing water pollution. For instance, organic livestock farming can enhance soil fertility through natural manure, fostering nutrient cycling. Furthermore, free-range systems often utilize less intensive farming strategies, leading to lower emissions per unit of animal protein produced. This aspect is particularly noteworthy as the livestock industry is a significant contributor to greenhouse gases. By adopting free-range and organic feeding practices, farmers play an essential role in combating climate change effects within agriculture. Supporting such farms can be an effective way to encourage environmental stewardship in food production, promoting a holistic approach to both animal husbandry and ecological care.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences for free-range and organic animal products continue to rise, driven by growing awareness of health and ethical concerns. Shoppers increasingly desire transparency in food sourcing, leading them to seek out products that reflect values aligned with wellbeing and sustainability. This demand puts pressure on conventional farming methods, encouraging a diversification in market offerings. As consumers become more discerning, labels like “certified organic” and “free-range” become integral to decision-making processes. The market for organic animal feed has expanded significantly, shaping competitive pricing dynamics and leading to innovations in production. Retail chains and restaurants that focus on quality animal welfare can often attract a loyal customer base, capitalizing on consumer demand. The trend translates into mainstream acceptance of the health benefits linked to organic products, with many willing to pay a premium for perceived quality. Notably, consumers are also more supportive of initiatives aimed at improving livestock conditions. Advocacy for better animal welfare standards has resulted in increased interest in local and sustainable farming practices. In turn, such trends signal a promising shift in the agricultural market towards more humane and environmentally friendly practices.
Feed formulation within free-range and organic systems differs significantly from conventional methods, often prioritizing whole grains and natural ingredients. These formulations are designed to meet specific nutritional requirements while adhering to organic standards. The focus on whole ingredients, such as legumes, seeds, and grains, results in a superior nutrient profile for animals. Additionally, access to pasture allows animals to consume a variety of plants, enhancing the dietary spectrum. This varied diet supports better gut health and nutrient absorption, which can ultimately lead to improved animal performance. Moreover, the rational use of supplements is crucial in these systems, as reliance on synthetic additives is discouraged. Natural supplements can provide essential vitamins and minerals that fortify the animals’ diets, ensuring robust health without compromising organic integrity. It’s essential to work closely with animal nutrition experts to develop feeding programs that maximize the benefits of free-range and organic diets. Farmers are encouraged to adapt their feeding strategies over time based on individual animal needs and environmental conditions. Regular assessment ensures that livestock maintain an optimal nutritional balance, promoting overall well-being.
Challenges in Implementation
While the benefits of free-range and organic animal feeding are clear, challenges persist in implementing these systems effectively. One of the primary hurdles is maintaining a consistent supply of quality organic feed. Farmers must establish reliable sources of organic grains and forage to support healthy livestock. This can be particularly challenging in regions where organic farming is not prevalent. Additionally, fluctuations in organic feed prices can impact the economic viability of adopting these methods on a larger scale. Moreover, space restrictions in certain livestock operations can limit the ability to provide true free-range conditions, leading to questions about the authenticity of certifications. It becomes increasingly important for farmers to develop innovative practices that comply with organic standards while also prioritizing space and movement for animals. Educating consumers about the importance of these factors is crucial in building trust in producers. Understanding certification processes and the significance of farming ethics can help shoppers make informed choices. Advocacy for supportive policies surrounding organic farming can also assist in overcoming these barriers, ultimately leading to a balanced agricultural landscape.
In conclusion, the science behind free-range and organic animal feeding reveals profound implications for animal welfare, ecosystem health, and consumer benefits. As research continues to illuminate the advantages of these practices, it becomes essential for farmers to embrace more sustainable methods to improve livestock husbandry. The connection between animal nutrition and health offers considerable insights into optimizing production while being ethically responsible. Consumers are now more informed and engaged with their food choices, reinforcing the need for transparency within the industry. The choice to buy organic or free-range products reflects a commitment to better animal welfare and environmental conscientiousness. Moreover, as market demand grows, so too does the potential for innovation in agriculture practices. Education is critical, as it empowers consumers to understand the real benefits behind their purchasing decisions. With demand for organic and sustainable practices on the rise, the agricultural sector must adapt to these shifting preferences. Ultimately, the synergy between animal nutrition, welfare, and consumer choice paves the way for a more equitable food system that benefits all stakeholders.