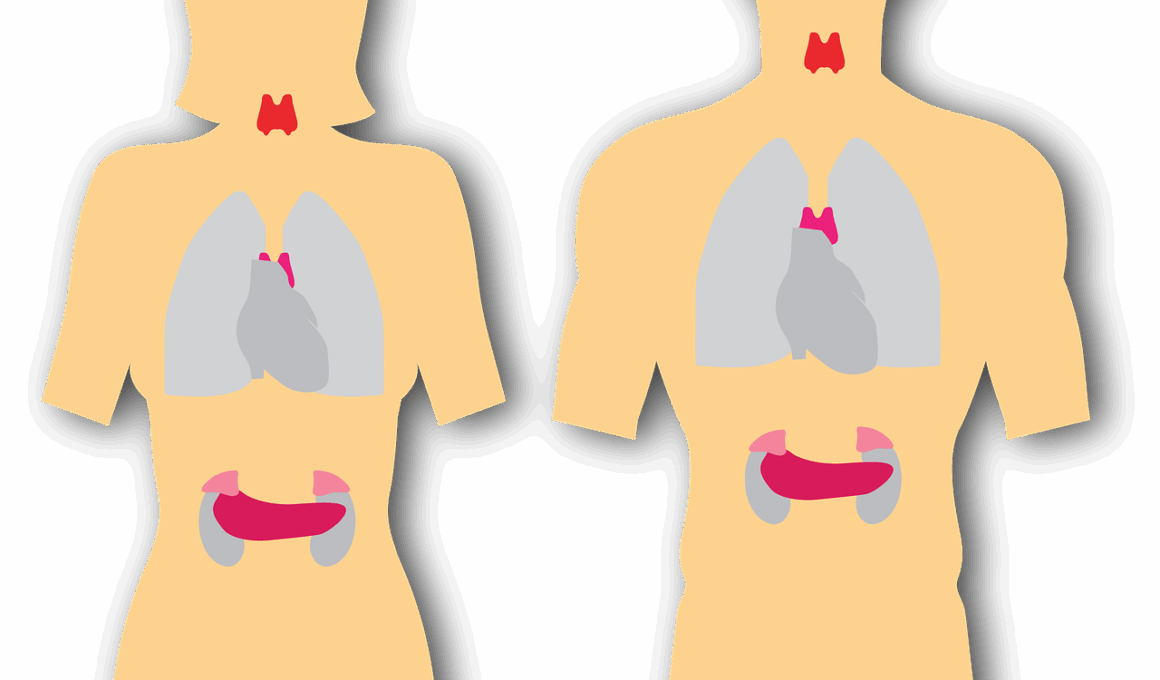Endocrine Disruptors Affecting Animal Health
The endocrine system plays a critical role in maintaining balance and regulating various bodily functions in animals. Hormones produced by glands such as the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands influence metabolism, growth, reproduction, and behavior. However, endocrine disruptors are chemicals that can interfere with this delicate system. These disruptors can mimic or block hormones, leading to adverse health effects. They can originate from various sources, including agricultural pesticides, industrial chemicals, and even some household products. Understanding their impact on animal health requires a multi-faceted approach. Researchers have identified specific endocrine disruptors, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), as significant threats. In wildlife and domesticated animals, these substances can lead to reproductive issues, abnormal development, and behavioral changes. Testing for these chemicals in the environment and in animal tissues is crucial to assess exposure levels and potential harm. Regulatory actions may be necessary to limit exposure and protect animal health. To mitigate these risks, promoting regulatory policies and increasing public awareness is vital.
In addition to wildlife, domesticated animals also face risks from endocrine disruptors. Livestock and pets are susceptible to the effects of these chemicals, often through contaminated feed or water supplies. Endocrine disruptors may compromise reproductive health, leading to lower fertility rates and impaired growth. Affected animals may exhibit changes in reproductive behaviors, leading to challenges in breeding programs. For instance, studies on cattle have shown that exposure to certain pesticides can result in altered estrous cycles, impacting pregnancy outcomes. Similarly, companion animals are at risk, with household products containing endocrine disruptors contributing to potential hormone-related health problems. Pet owners need to be aware of ingredients in various products, including cleaners and grooming supplies, to minimize exposure. Furthermore, dietary choices can also lead to endobiotic exposure, as some livestock may be fed grains treated with harmful substances. It is essential to monitor these factors and educate animal owners on safer alternatives. Veterinary professionals play a vital role in diagnosing and treating conditions caused by endocrine disruptors and educating pet owners on minimizing risks associated with these chemicals.
Mechanisms of Endocrine Disruption
The mechanisms through which endocrine disruptors affect animal health are complex and multifaceted. These chemicals can interact with hormone receptors and interfere with normal hormonal signaling. For example, they may bind to estrogen receptors, mimicking estrogen’s effects, which can lead to reproductive and developmental disorders. In some cases, endocrine disruptors can also disrupt the synthesis and metabolism of hormones, leading to an imbalance. This imbalance can exacerbate the effects of natural hormones, resulting in altered physiological responses. Furthermore, endocrine disruptors can affect gene expression, leading to long-term developmental changes that may persist across generations. Research continues to identify the pathways affected by these chemicals, highlighting their potential for chronic health issues. For instance, exposure to certain pesticides has been linked to increased risks of tumors and developmental abnormalities. Additionally, environmental factors such as temperature and nutrients can influence the severity of endocrine disruption. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for developing mitigation strategies and ensuring the health of domestic and wild animal populations. Ongoing research aims to uncover the full extent of these interactions to better inform regulatory decisions.
Monitoring the environmental presence of endocrine disruptors is essential for safeguarding animal health. Environmental testing can identify contamination levels in water, soil, and feed, allowing for better assessment of potential risks. Regular monitoring helps to track the effectiveness of regulatory policies and identify emerging threats. Implementing effective sampling techniques and analyzing data can provide insights into the most hazardous areas and demographics. For example, testing fish populations for contaminants can lead to discovering broader ecosystem health issues, which can ultimately impact animal welfare. Collaborative efforts among scientists, governments, and conservation organizations are necessary to facilitate such monitoring initiatives. Education and outreach programs can also play a crucial role in informing agricultural producers about responsible chemical use and best management practices. Promoting organic farming methods and the use of alternatives to synthetic chemicals can significantly reduce the risk of endocrine disruption. Stakeholders must work together to ensure laboratory-tested products are accessible and affordable. In addition, public awareness campaigns can encourage community involvement in conservation efforts. By fostering an understanding of the importance of monitoring endocrine disruptors, communities can actively support initiatives that promote animal health.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks
In response to the threats posed by endocrine disruptors, various strategies can be implemented to mitigate risks to animal health. First, regulatory agencies are crucial in enforcing policies that limit the use of harmful chemicals. Stricter regulations can help prevent the entry of new endocrine disruptors into the market. Incentives for using alternative substances can also be effective in promoting safer agricultural practices. Educating veterinarians and animal owners on potential risks is vital. Providing resources that better inform pet and livestock owners about the importance of chemical safety can lead to more informed choices. Additionally, transparency between manufacturers and consumers regarding the ingredients in animal products can foster a more educated public. Establishing partnerships between scientists and policymakers ensures that research informs regulations effectively. Veterinarians must also play an active role in diagnosing and advocating for animals affected by endocrine disruptors. Continued research into safer alternatives can also facilitate reducing reliance on harmful chemicals in agriculture and animal care. Building awareness about the significance of animal health and the threats posed by endocrine disruptors can galvanize collective action among concerned stakeholders.
Public awareness can significantly influence consumer behavior and demand for safer products. When consumers prioritize animal health over convenience, manufacturers are incentivized to develop chemical-free alternatives. Campaigns that raise awareness about the harmful effects of endocrine disruptors can drive change in purchasing habits. Consequently, businesses may feel compelled to invest in sustainable practices that prioritize both animal welfare and environmental health. Furthermore, engaging with advocacy groups can amplify these voices, highlighting the economic benefits of adopting safer practices. Collaborating with local farmers to promote sustainable farming methods can also enhance community involvement. Educational initiatives that involve local schools can help inform future generations about the impacts of chemicals on animal health. Offering resources for sustainable lifestyle choices, from pet care to agricultural practices, encourages community empowerment. Community forums can serve as platforms for discussion, fostering dialogue between consumers, farmers, and scientists. In conclusion, creating a movement towards safer alternatives requires collaboration among stakeholders, public awareness, and a collective commitment to reducing the impact of endocrine disruptors on animal health.
Future research will be crucial in understanding endocrine disruptors and their effects on animal health. Striving for innovative solutions to mitigate these risks is an ongoing endeavor in scientific communities. Improved methodologies for testing and assessing the impact of these substances will enhance our understanding of their effects on various species. Longitudinal studies can provide detailed insights into chronic exposure and its consequences over time. More attention should also focus on the cumulative effects of multiple endocrine disruptors, as combined exposure can pose greater risks. Interdisciplinary collaborations can illuminate how these disruptors affect different systems within the animal body. Funding for research on developing safer alternatives is vital to establish sustainable practices moving forward. Identifying potential biomarkers for early detection of endocrine disruptor exposure will help manage animal health proactively. Educational programs can instill a commitment to research in younger generations, leading to more innovative approaches in the future. By prioritizing research and knowledge development, scientists can pave the way for healthier animal populations and minimize the risks posed by endocrine disruptors.
The role of veterinarians in combating the effects of endocrine disruptors cannot be overstated. They are essential in educating pet owners about the symptoms and potential risks associated with exposure to harmful chemicals. Early diagnosis of endocrine-related disorders can significantly improve treatment outcomes and animal well-being. Veterinary clinics can implement screening programs to identify pets at risk of exposure, thereby providing guidance on reducing contact with endocrine disruptors. Additionally, supporting continued education programs for veterinary professionals is important. By staying informed about the latest research and treatment modalities, veterinarians can effectively protect animal health. Integrating discussions about environmental health into routine veterinary practice can promote awareness among clients. As advocates for animal welfare, veterinarians play a crucial role in lobbying for regulations that support healthier environments for animals. Collaborative research efforts between vets and scientists can also lead to new insights into the effects of endocrine disruptors. In the long term, building conducive frameworks for responsible use of chemicals in veterinary practice ensures a safer future for both pets and livestock. Enhanced advocacy and community engagement within this profession will foster a culture prioritizing animal health and environmental sustainability.