Communication Methods and Language Skills in Primates
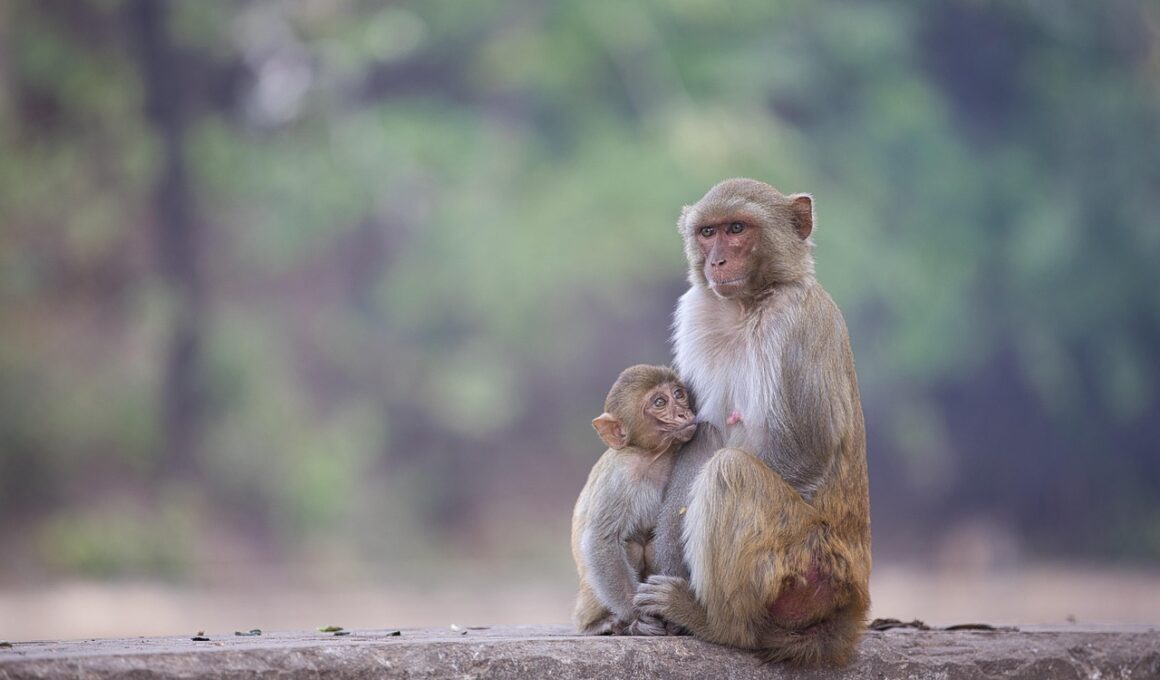
Communication is a vital aspect of life for primates, playing an essential role in their interactions. Various species of primates exhibit a wide range of communication methods that highlight their remarkable intelligence. Among these species, chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans have shown not only the ability to use sounds but also the capacity to incorporate gestures, facial expressions, and body postures into their communication repertoire. They utilize vocalizations to express emotions, alert others to dangers, or indicate food availability. These vocalizations can vary in pitch and intensity, granting them complexity. Moreover, many studies reveal that primates develop unique calls or sounds specific to their social groups, indicating cultural transmission among them. This cultural aspect of communication illustrates that primates are not only intelligent beings but also possess the ability to learn from one another. In addition, researchers have documented the use of tools in their communication efforts, such as utilizing sticks to point towards objects of interest. Such actions underscore the versatility of primate communication, highlighting their capacity for abstract thinking and problem-solving. These features not only aid in their survival but foster social bonds.
The advancement in research on primate communication offers groundbreaking insights. Primates utilize various forms of communication that extend beyond mere vocalizations. For instance, body language plays a significant role in how they convey messages across different species. Gorillas often use hand gestures, while chimpanzees display complex facial expressions to communicate their emotions or intentions. Furthermore, many primates engage in social grooming, a behavior that fosters bonds between individuals and acts as a mode of silent communication. This grooming behavior is essential in maintaining social hierarchies and alliances. In addition, the presence of regional dialects among different primate groups indicates their ability to adapt their communication based on social environments. Researchers have recorded instances where primates incorporate new sounds or modify their communication methods in novel situations. This adaptability is vital for their survival in changing habitats. Understanding these communication methods enhances our appreciation for primates’ cognitive abilities and their intricate social structures. Observing these behaviors allows scientists to explore intelligence and assess how primates navigate their social worlds. Thus, communication remains a fascinating area of study in understanding primate intelligence and social dynamics.
The Role of Symbolic Communication
Symbolic communication is a significant aspect of language skills in primates. Researchers have conducted experiments to determine whether primates can understand symbols and use them to communicate effectively. Notably, studies involving chimpanzees trained to recognize symbols have shown promising results. These chimpanzees can associate specific symbols with objects or concepts, indicating a high degree of cognitive flexibility. For example, a well-known case involved Kanzi, a bonobo who learned to use a lexigram board, allowing him to communicate his needs. Initially, handlers employed a reward system to motivate Kanzi, which gradually led to his understanding of symbolic meanings. This demonstrates that some primates can extend their communication beyond simple gestures or sounds, tapping into a more complex linguistic form. Moreover, as they learn and use symbols, it indicates not only intelligence but also the potential for cultural evolution within their species. Engaging in symbolic communication provides a window into exploring the cognitive capacities of primates, shedding light on the evolutionary roots of language. These valuable insights into primate communication methods can bridge understanding between human language formation and primate communication.
Another fascinating area of research is the study of how primates use their communication methods in social contexts. In their natural habitats, primates often face various challenges requiring sophisticated communication to navigate social relations. For example, the concept of deception is observed among some primate species; they can use misleading vocalizations to redirect attention away from themselves. This ability to manipulate information showcases not only their intelligence but also their understanding of the social environment. Social networks within primate habitats are intricate, shaped by constant interactions requiring effective communication. Different primate species may employ a variety of calls specific to their social scenarios to maintain order within their groups. Furthermore, cooperative behaviors are enhanced through clear and intentional communication, reflecting the fundamentals of social intelligence. Observations have illustrated that primates who engage more actively in communication often have better access to resources and mates. The necessity for effective communication in ensuring individual and group success highlights the integral nature of these skills in primate societies. These findings underscore the significance of studying communication in understanding primate intelligence, emphasizing its importance in their social dynamics.
Sign Language and Communication Training
One of the most intriguing developments in the study of primate communication is the successful teaching of sign language to some species. Research has shown that chimpanzees and gorillas can learn sign language, enabling them to interact with humans on a more profound level. A significant case is that of Koko, a gorilla who was taught American Sign Language (ASL) and could express various thoughts, feelings, and needs through signs. Koko’s handlers recorded countless instances of her effectively communicating complex ideas, such as expressing grief over her pet cat’s death or joy in playful interactions. These experiences demonstrate the potential for primates to understand human concepts and articulate their own, reinforcing their intelligence. Moreover, this signing capability has prompted further investigations into how primates conceptualize language and their potential for more advanced communication forms. By examining their learning processes and subsequent use of sign language, researchers gain insights into cognitive development aspects shared between humans and primates. This research underscores the importance of the vocabulary primate species create, providing invaluable knowledge regarding the evolution of language and its role in intelligent beings.
The implications of language skills and communication methods in primates extend beyond understanding their social behaviors. They provide vital clues about evolutionary biology and the origins of human language. Insights gained from primate communication studies can inform theories about how early human ancestors might have developed language. By exploring the parallels between human and primate communication, researchers aim to uncover how language evolved and what cognitive capacities are essential for it. For instance, the use of gestures among primates may mirror early human communication systems. Connections between gestures and vocalizations in communicative intent highlight a possible evolutionary trajectory leading to human language. Furthermore, understanding the neural mechanisms underpinning these communication methods can contribute to our knowledge of how the brain processes language and meaning. Since primate brains share structural similarities with human brains, studies focusing on their language capabilities and communication offer valuable insights. By establishing links between sociality, communication, and intelligence, the science of animal linguistics opens avenues for further exploration of the intricate relationship between language, culture, and evolution, enriching our understanding of ourselves.
Conclusion: The Importance of Communicative Skills
In conclusion, exploring communication methods and language skills in primates reveals the complexity of their social networks and cognitive abilities. From vocalizations to symbolic gestures, primates exhibit a diverse array of communication forms, demonstrating their intelligence and adaptability. The ability to convey messages effectively influences their success in navigating their environments, forming social bonds, and maintaining group cohesion. Studying these communication methods not only sheds light on primate behavior but also enhances our understanding of language evolution. As researchers unravel the intricacies of primate communication, they delve into the shared history of humans and primates, examining the foundations of language development. The significance of these studies cannot be overstated; they offer crucial perspectives on intelligence, social structures, and our own communication systems. Future research endeavors should aim at exploring lesser-known primate species to gain a comprehensive understanding of the full range of communicative skills. Through ongoing observations and experimentation, scientists will continue to illuminate the intertwining narratives of primate language and intelligence. Ultimately, the continued exploration of these topics provides invaluable insights into the cognitive worlds of primates.
Researchers have long been fascinated by communication methods among primates, emphasizing their language skills. Understanding these communication forms enhances our insight into the evolution of intelligence. For instance, despite no formal education, several primates comprehend complex communication strategies, which reflect their cognitive capabilities. The nuances of their vocalizations are crucial to their survival. Vocalizations serve various purposes; they warn group members of dangers, coordinate hunting approaches, and even convey emotions like joy or grief. The ability to communicate abstract concepts has intrigued researchers, leading to various studies showcasing this intelligence. In both natural habitats and captivity, primate communication reveals a rich tapestry of social interactions. Additionally, many primate groups demonstrate unique communication styles, further emphasizing the intricate cultural dynamics within them. The discovery of gestures, facial expressions, and postural language demonstrates a realm of communication that surpasses simple vocalizations. This interplay of different methods of communication highlights their social sophistication and adaptability. Moving forward, ongoing studies must prioritize understanding the impact of environmental change on these communication methods. Such research could lead to valuable insights into the flexibility of primate communication skills.