The Significance of Porcupine Herbivores in Biodiversity
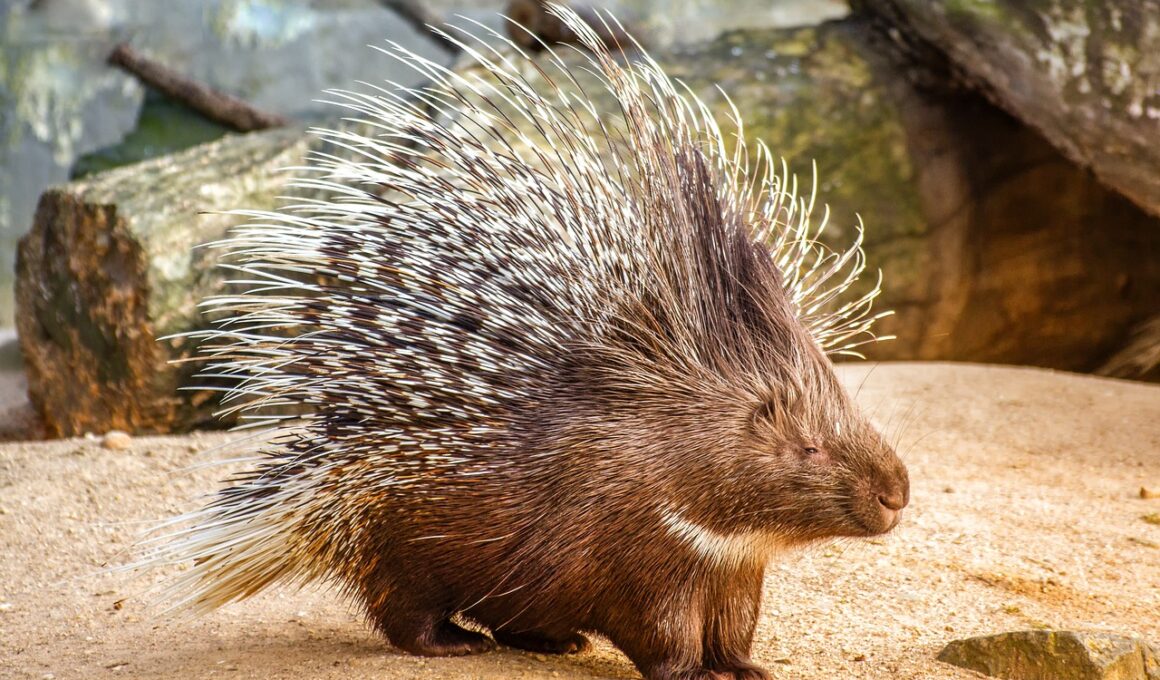
Porcupines are intriguing creatures within the herbivore category, playing a vital role in the ecosystem. These animals primarily thrive in forested and woodland areas, where they exhibit unique feeding habits. A porcupine’s diet mainly consists of leaves, bark, and fruits, contributing to the regulation of tree populations in their habitats. This governing effect helps to maintain balance, allowing various species to flourish. Interestingly, their foraging behavior encourages the growth of new plant life, as they tend to eat older branches, allowing sunlight to reach the younger plants below. As a result, the biodiversity of their environments significantly increases. In this way, porcupines exemplify how herbivores can act as environmental engineers, promoting a diverse range of flora. Their feeding habits not only influence plant communities but also impact the animal species that rely on these plants for food and shelter. Moreover, other small mammals and birds benefit from the habitat changes that porcupines create. Maintaining healthy populations of porcupines assists in the overall biodiversity of ecosystems, ensuring ecological stability across various landscapes.
Research shows that porcupines also play a crucial role in biodiversity in subtler ways. As these animals forage through their habitats, they inadvertently spread seeds through their feces. This process aids in the proliferation of various plant species, contributing to genetic diversity within woodland ecosystems. Additionally, by feeding on trees, porcupines can enhance the growth of herbaceous plants by creating open spaces for them to flourish. Such dynamics are essential, as rich biodiversity is beneficial for various wildlife species, providing food and shelter. For example, many bird species utilize the trees that porcupines feed on, as these trees provide necessary nesting sites and food sources. Furthermore, the dismantling of old bark and branches by porcupines creates diverse habitats for smaller insects and other invertebrates. The relationships among these organisms enhance ecosystem functionality and resilience. Consequently, understanding the impact of porcupines on biodiversity prompts conservation efforts to protect their populations. As they face various threats, including habitat loss, protecting porcupines is critical to preserving ecological balance.
Conservation of Porcupines and Their Role
Conserving porcupine populations is not just about protecting a single species but is crucial for preserving the intricate web of life they support. Various human activities lead to habitat degradation, which endangers their existence. Deforestation, urban development, and agricultural expansion significantly encroach on their habitats, threatening their survival. Conservation efforts must focus on habitat preservation and restoration to ensure porcupines continue to thrive. Educating communities about the importance of these creatures can improve the conservation outlook. Responsible forestry practices, wildlife corridors, and legal protections for their habitats are essential components of a comprehensive conservation plan. Moreover, local communities can engage in wildlife conservation projects, helping to monitor porcupine populations and educate others on their ecological significance. When communities join in conservation efforts, they create a vested interest in the biodiversity surrounding them. In so doing, they help ensure that future generations can also benefit from robust ecosystems. Sustainability and awareness are crucial to securing the future of porcupines and the critical roles they play in promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health.
The influence of porcupines extends beyond their immediate environment; they can affect larger ecological processes. By feeding on certain trees, porcupines’ preferences shape forest structure and species composition. Their selective feeding helps maintain dynamic ecosystems, where various species coexist and interrelate. Consequently, this balance is pivotal for larger herbivores that may depend on the same vegetation. For instance, deer populations might increase in areas where porcupine activity enriches the availability of understory plants. This phenomenon correlates to a positive feedback loop, where diverse plant life supports greater herbivore populations, fostering wildlife interactions and promoting a vibrant ecosystem overall. Furthermore, other wildlife, including predators, benefit from the prey these thriving herbivores provide. Such factors underline the interconnectedness found in ecosystems, emphasizing the importance of each species in maintaining biodiversity. Protecting porcupines ensures that these ecosystems can continue to thrive, with every creature ultimately relying on the health and stability of their environment. Awareness campaigns and conservation initiatives can amplify their significance, fostering greater appreciation and protective measures for their well-being.
The Importance of Habitat Diversity
Porcupines thrive in habitats rich in diversity, which amplifies their role in boosting biodiversity. They primarily inhabit regions featuring a mix of coniferous and deciduous trees, allowing for a varied diet that consists of bark, leaves, and fruits. The consumption of different plant types results in a mosaic of habitats that benefits numerous species. Healthy porcupine populations promote habitat diversity, further fostering resilience against environmental change. Unique habitats encourage variation in plant life, which in turn supports diverse insect communities. These insects nourish birds and other small mammals, illustrating the critical connections in food webs. A balanced and diverse environment helps maintain the stability of ecosystems against invasive species and climate fluctuations. To ensure habitat diversity thrives, porcupine conservation must prioritize forest management practices that prevent habitat fragmentation. Promoting controlled logging and sustainable practices can enhance habitat availability, creating areas conducive for porcupines and other wildlife. Encouraging biodiversity at every level ultimately strengthens ecosystems and underscores the essential role herbivores play, with porcupines serving as a keystone species within this context. By focusing on habitat preservation, we can safeguard their invaluable contributions to biodiversity for years to come.
Porcupines also serve as indicators of environmental health and climate change. Given their sensitivity to habitat loss and changes in vegetation, monitoring their populations can provide insights into broader ecological trends. For instance, a decline in porcupine populations may reflect broader environmental problems, such as pollution or habitat degradation. By studying their reactions to changing environments, scientists can gauge the effectiveness of conservation efforts and adapt strategies accordingly. Porcupines can also help in assessing the overall health of their ecosystems based on their dietary preferences and population dynamics. Their prominent roles in seed dispersal and their interactions with other species highlight their environmental significance. Communities invested in monitoring these creatures can participate in citizen science initiatives, engaging actively in wildlife conservation. Tools such as wildlife cameras, community surveys, and tracking projects can yield important data on porcupine behavior and populations. Public interest in these initiatives can foster a deeper connection between people and the environment, ultimately leading to enhanced conservation awareness. Increased research on porcupines and their ecosystems can further illuminate the interconnectedness of biodiversity, demonstrating the vast implications of each species and the ecological roles they fulfill.
Final Thoughts on Porcupine Herbivores
The significance of porcupines transcends their role as herbivores; they exemplify the delicate balance found in nature. As essential players in forest ecosystems, porcupines help maintain biodiversity through their feeding behaviors and habitat alterations. This intricate relationship underlines just how valuable each species is in contributing to the stability and health of ecosystems. Their interactions with the flora and fauna they share their environment with illustrate the cascading impacts that herbivores can have on biodiversity. As we continue to face environmental challenges, upholding healthy porcupine populations becomes vital for ecological restoration efforts. Moreover, embracing sustainable practices can mitigate potential threats to porcupines and ensure the longevity of the ecosystems they support. Encouraging communities to engage in conservation efforts not only benefits porcupines but also enhances the overall ecological awareness of individuals. Protecting these remarkable creatures means safeguarding our ecosystems and preserving the very essence of biodiversity. In conclusion, investing in porcupine conservation holds the key to fostering greater resilience within our natural habitats, paving the way for balanced ecosystems that thrive harmoniously.
Thus, porcupines emerge not simply as fascinating creatures in their own right but also as significant contributors to biodiversity, deserving our utmost attention. As stewards of their habitats, porcupines exemplify how interconnected life is within ecosystems. Observing their behavioral dynamics can evoke a sense of wonder and appreciation for nature’s intricacies. Furthermore, their role in maintaining plant diversity and the habitats that support other wildlife contributes to the vibrancy of our natural world. It is increasingly evident that each species, no matter how small, plays a role in ecological balance and health. The preservation of porcupines, along with their habitats, becomes a commitment we owe to future generations. Each conservation effort must celebrate their intrinsic value, forging stronger connections between people and wildlife. Collaborative projects can involve schools, nature groups, and researchers in ongoing initiatives that promote understanding and appreciation for these herbivores. Together, we can champion a world where porcupines continue to roam and thrive, enriching our ecosystems and inspiring awe as part of our shared natural heritage.