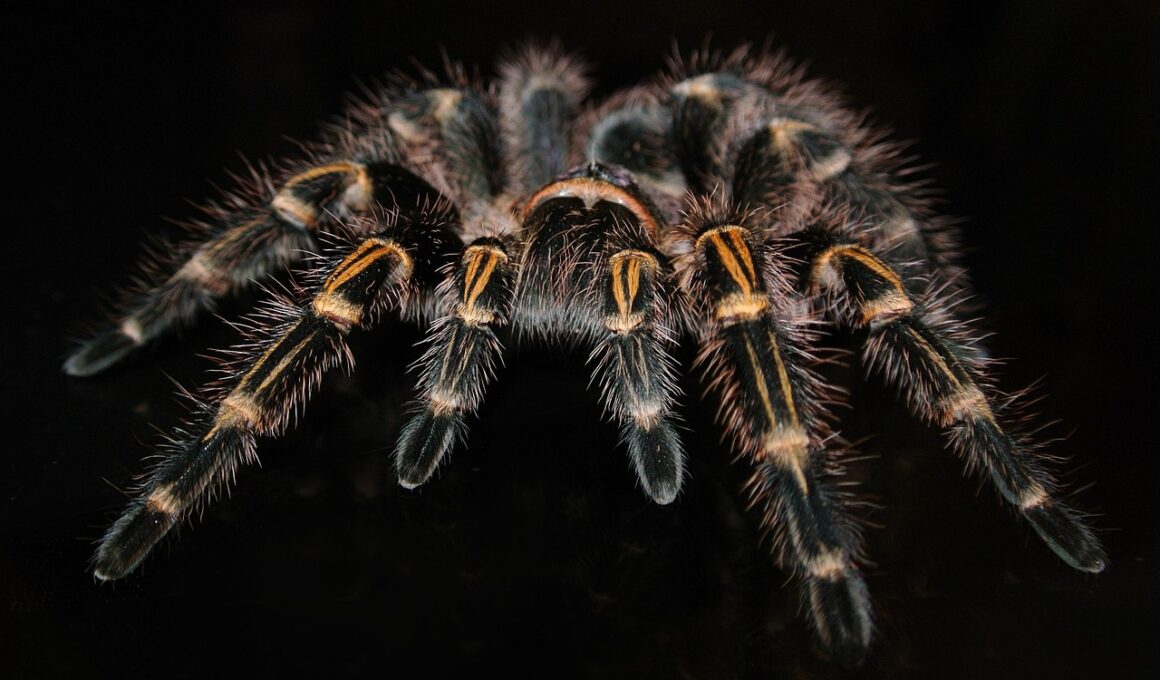
Conserving Tarantulas: Challenges and Opportunities
Tarantulas pose a unique conservation challenge due to their vital ecological role and the growing threats they face. These fascinating arachnids contribute to controlling insect populations, serving as both predator and prey in their ecosystems. Unfortunately, habitat loss, driven primarily by human activities such as urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation, has been detrimental to tarantula populations. They are also collected for the exotic pet trade, leading to further declines. Education is crucial for their conservation, as many people do not understand the ecological benefits of tarantulas. Conserving their habitats can involve multiple strategies such as creating protected areas, promoting sustainable land use, and increasing public awareness of these misunderstood creatures. Furthermore, research is essential to understand their life cycles, behaviors, and the specific requirements for their survival. International collaboration is often needed, as tarantula species are distributed across various countries and ecosystems. Conservation efforts can succeed by involving local communities, giving them incentives to protect these spiders while educating them about their importance. Emphasizing the positive ecological roles that tarantulas play can foster a more responsible attitude towards their preservation.
Understanding Tarantula Behavior and Ecology
Understanding tarantula behavior and ecology is vital for effective conservation strategies. This involves studying their natural habitats, breeding patterns, and dietary habits to ensure informed decision-making. Tarantulas primarily inhabit tropical or subtropical regions, where they thrive in various environments, including rainforests, grasslands, and deserts. They exhibit unique behaviors that include burrowing and web-spinning, which allow them to recreate suitable microhabitats. Their diet mainly consists of insects, but larger species may prey on small mammals and birds. Recognizing the significance of these behaviors helps ascertain necessary conditions for their survival. Additionally, tarantulas have fascinating reproductive patterns, with some species displaying sexual dimorphism. Female tarantulas tend to live longer than males, which influences population dynamics. Conservation programs must emphasize the direct connection between their behavior, habitat needs, and survival. By understanding aspects of their life cycles, including mating rituals and juvenile development, we can better accommodate their needs in conservation initiatives. Involving behavioral ecologists and biologists in research projects can greatly benefit conservation strategies, providing essential data to inform actions. Prioritizing behavioral studies can ultimately help lead to more successful tarantula conservation outcomes.
Habitat protection is a significant aspect of tarantula conservation, ensuring that these creatures can thrive in their natural environments. Efforts to establish and maintain protected areas help preserve essential habitats that support diverse flora and fauna, including tarantulas. Conservationists advocate for policies that prioritize ecosystem preservation, recognizing the interdependence of various species. Implementing sustainable practices within agricultural landscapes can help to minimize habitat destruction, providing a balance between human needs and environmental health. Responsible land-use practices can create wildlife corridors, allowing species to access resources and migrate safely. Furthermore, habitat restoration initiatives can rehabilitate degraded land, making it suitable for tarantula populations once again. Collaborating with local communities ensures that these conservation strategies align with their needs and benefits, fostering a sense of ownership among residents. Encouraging ecotourism can create economic incentives for protecting tarantula habitats, generating funds for conservation efforts. Enhancing public awareness campaigns about the importance of tarantulas in ecosystems can galvanize support for habitat protection. Overall, focused actions on habitat conservation can significantly impact the survival and prosperity of tarantula populations, promoting a healthy balance in local ecosystems.
Combatting the Pet Trade
The exotic pet trade poses a significant threat to tarantula populations worldwide, necessitating urgent interventions and strategies to combat this issue. Many species are captured from the wild, leading to drastic population declines and threatening their survival in their natural habitats. Awareness-raising campaigns are critical to inform potential pet owners about the implications of adopting tarantulas, and promote ethical sourcing from reputable breeders. Establishing regulations and ensuring compliance to control the trade of rare and endangered tarantula species can have a positive effect on their conservation. Collecting data on the numbers of tarantulas traded, species sold, and their provenance is vital for evaluating the impact of this trade. Engaging with legal authorities and organizations is necessary to enforce laws that protect tarantulas from illegal poaching and trade. Non-governmental organizations can play a key role in advocating for stricter regulations and providing education to local communities about sustainable practices. Supporting captive breeding programs can create alternatives to wild capture, ensuring that pet owners can responsibly enjoy tarantulas while contributing to conservation initiatives. This synergistic approach can help mitigate the risks of the exotic pet trade for tarantulas.
Community involvement is essential for the success of tarantula conservation efforts, as local populations can greatly influence the outcomes of initiatives. Engaging communities in educational programs can foster a better understanding of the ecological benefits of tarantulas, dispelling myths and fears surrounding these spiders. Workshops, informational brochures, and school seminars can raise awareness about their role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. Forming partnerships with local organizations can help provide resources and support for conservation projects. Additionally, creating opportunities for ecotourism allows communities to share in the economic benefits of conservation, increasing both participation and commitment to protecting tarantula habitats. This collaboration can also encourage unique cultural practices that respect local wildlife, fostering coexistence between humans and tarantulas. Integrating indigenous knowledge into conservation strategies ensures that local wisdom and practices are respected and utilized. Moreover, establishing citizen science projects can empower community members to contribute to data collection and monitoring efforts. These initiatives encourage a sense of stewardship and personal responsibility regarding local wildlife. When communities feel a personal connection to their environment, they are more likely to support conservation efforts and protect the species that inhabit it.
Research and Conservation Collaboration
Research collaboration is a cornerstone of successful tarantula conservation, enhancing our understanding of these complex creatures and their ecology. By working together, scientists, conservationists, and local communities can create more robust conservation strategies based on solid data. Collaborative research initiatives can include habitat assessments, population monitoring, and genetic studies to understand the health of tarantula populations. Sharing findings across disciplines can provide critical insights into the threats they face and how best to address them. This interdisciplinary approach strengthens conservation actions, as it combines varying expertise, technologies, and methodologies. Facilitating partnerships with universities and research institutions can generate funding and resources to support long-term studies on tarantula conservation. Furthermore, collaboration can yield better public communication strategies, allowing projects to reach broader audiences. Highlighting success stories can inspire others to engage in tarantula conservation efforts. Engaging students in research programs fosters the next generation of conservationists and ecologists. Showcasing these partnerships through effective outreach can strengthen community support for ongoing initiatives, making conservation efforts sustainable. Ultimately, a collaborative research focus can lead to innovative solutions and better conservation outcomes for tarantulas.
In conclusion, the conservation of tarantulas presents both challenges and opportunities that require a multifaceted approach. It is essential to raise awareness about the ecological roles they play and the threats they face in a rapidly changing world. Support from local communities and global advocates is vital to fostering sustainable practices that prioritize habitat preservation. Education campaigns can reduce misconceptions, creating a more favorable environment for tarantula conservation. Furthermore, tackling issues related to the exotic pet trade is crucial, as well as implementing community-led initiatives that promote ethical practices. Research plays a critical role in informing and guiding conservation efforts, and collaboration among various stakeholders will strengthen this response. Captive breeding initiatives can provide alternatives to wild capture while contributing to population stability. By working together, we can enhance our understanding of tarantula biology and behavior, ultimately leading to better conservation strategies. Future efforts must balance ecological needs with human interests, fostering a coexistence that benefits both species and habitats. With commitment and coordinated actions, tarantula conservation can not only be achieved but can also serve as a model for preserving other endangered species across the globe.