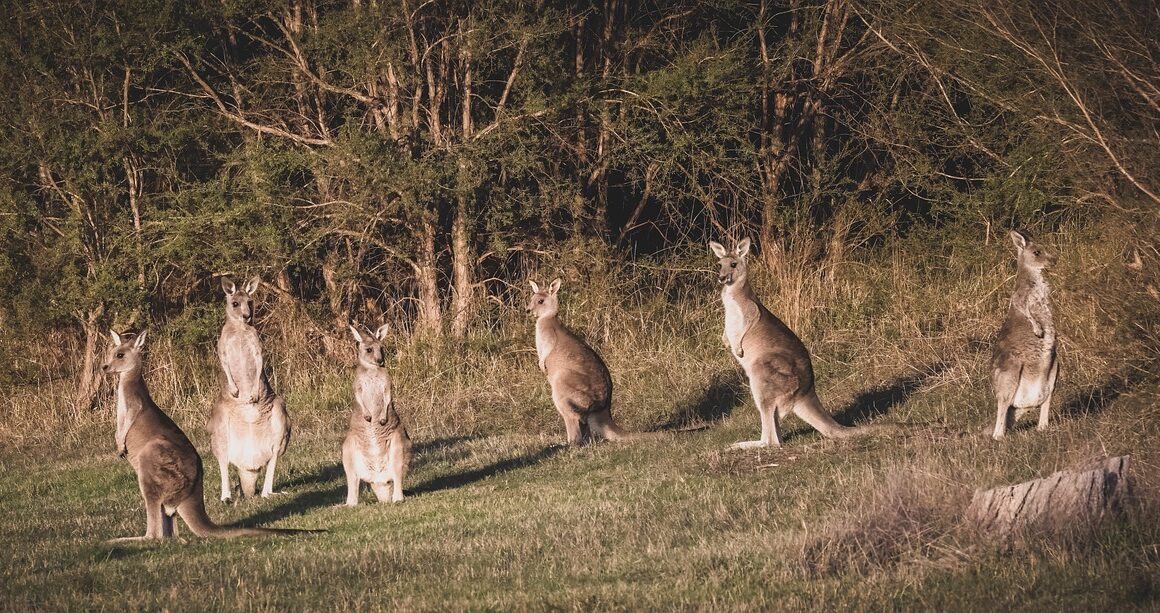
Assessing Habitat Connectivity for Marsupial Movement
Understanding habitat connectivity is crucial for the conservation of marsupial populations across diverse ecosystems. The fragmentation of habitats due to urbanization and agriculture poses significant threats to these unique creatures. Without properly connected habitats, marsupials struggle to find food, mates, and shelter. This can result in decreased genetic diversity and increased mortality rates. To counter these challenges, researchers study various ecological corridors that facilitate safe marsupial movement. These corridors must be large enough to allow species to traverse safely while also being ecologically viable. Identifying these areas requires comprehensive data that characterizes both biological needs and landscape features. Additionally, conservation efforts need to incorporate community awareness and stakeholder engagement to advocate for habitat preservation. By prioritizing connected landscapes, we enhance the chances of marsupial populations thriving in the wild. This not only benefits marsupials but also fosters biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem health. As scientists and conservationists collaborate to create effective strategies, the role of technology in mapping and monitoring habitat connectivity becomes increasingly significant in this endeavor.
Importance of Ecological Corridors
Ecological corridors are essential for ensuring the survival of marsupials in fragmented environments. These are natural pathways that connect different habitats, allowing animals to move freely and safely between areas. In a world where climate change and human development are altering landscapes, these corridors can mitigate the impacts of habitat loss. For marsupials, the ability to move between habitats influences their access to critical resources and opportunities for reproduction. Moreover, conducting thorough assessments is vital for identifying potential corridors that enable species to adapt to changing environmental conditions. This requires a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating ecological, geographical, and technological research methodologies. Such assessments also emphasize the significance of preserving existing habitats while enhancing connectivity across fragmented landscapes. Furthermore, engaging local communities is paramount in establishing these ecological corridors. Public support can lead to effective conservation initiatives that ensure the long-term viability of marsupial populations. By raising awareness and fostering understanding of these ecological corridors, stakeholders can collectively work towards creating a more sustainable environment that supports biodiversity. Through these efforts, we aim to provide marsupials with the necessary means to thrive and navigate their changing habitats.
While assessing habitat connectivity, it is crucial to understand the movements and behaviors of marsupials in response to these ecological features. Different species exhibit varying levels of mobility and habitat preferences, necessitating specific considerations for successful corridor designs. For instance, smaller marsupials may require narrower pathways compared to larger species that may utilize broader corridors. This variability indicates that no one-size-fits-all approach exists when determining effective strategies to connect habitats. Field studies using telemetry and tracking technologies can yield invaluable insights into movement patterns. Collecting this data helps identify current barriers and facilitators of movement, enabling researchers to formulate effective solutions tailored to each species. Another important aspect to consider is the presence of human-made infrastructures, such as roads or fences. These obstacles can severely hinder marsupial movement; hence addressing these through innovative conservation measures becomes critical. Landscape management practices may include constructing wildlife crossings or maintaining natural vegetation along pathways to enhance connectivity. By addressing these areas of concern, conservation initiatives can significantly improve the chances of successful marsupial migration and, ultimately, ensure better survival rates.
Challenges in Habitat Assessment
The challenges associated with habitat assessments for marsupial populations are numerous and complex. One major obstacle is the lack of comprehensive and up-to-date data regarding land use and habitat conditions. Often, existing maps do not reflect the current state of the ecosystem, making it difficult for researchers to develop accurate models for connectivity. Furthermore, quantifying the ecological requirements of different marsupial species is a significant research challenge. Different marsupial species exhibit unique behaviors, ranging from dispersal patterns to habitat preferences, necessitating species-specific data collection. Additionally, climate change adds a layer of uncertainty, affecting habitat availability and quality. This dynamic environment continually reshapes the geophysical landscape, further complicating connectivity assessments. Researchers must constantly adapt their methodologies to account for ongoing changes to ecosystems. Furthermore, there is the challenge of balancing conservation goals with landowners’ rights and developmental interests. Collaborative efforts between scientists, conservationists, and local communities are essential to create a more cohesive approach to conservation that respects both ecological and human needs.
In addition to addressing the challenges of assessment, engaging in participatory research can significantly enhance the outcomes of habitat connectivity studies. Involving local communities in the research process allows for the gathering of diverse perspectives and data, cultivating a sense of ownership and advocacy for wildlife conservation initiatives. Workshops, citizen science programs, and outreach activities can educate the public about the importance of marsupial habitat connectivity. These interactions foster strong relationships between scientists and local communities, leading to better-informed conservation actions. State policies and regulations should also evolve to support these kinds of collaborative efforts. Moreover, integrating modern technology like remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS) enables researchers to visualize habitat connectivity more effectively. Such technologies provide valuable insights into landscape features that hinder or facilitate marsupial movement. Ultimately, harnessing community engagement coupled with advanced technological tools can lead to more robust conservation strategies that promote sustainable habitat management. This approach reinforces the idea that successful conservation requires collective effort, where each stakeholder plays a vital role in preserving the ecological balance.
Future Directions for Research
Looking ahead, research on marsupial habitat connectivity must continually evolve to address emerging challenges and adapt to changing circumstances. Future studies should prioritize incorporating climate resilience into connectivity assessments, ensuring that corridors can withstand environmental fluctuations. This includes considering how extreme weather events or gradual changes in temperature and precipitation patterns might impact marsupial movements and habitat utilization. Furthermore, research should explore innovative techniques such as genetic analysis to assess the health and viability of isolated populations. Understanding the genetic diversity in fragmented habitats may inform corridor design, emphasizing areas that promote genetic exchange. Collaborations with technology and engineering fields can facilitate the development of effective solutions like wildlife overpasses or underpasses. By working together, various disciplines can provide unique insights into creating sustainable landscapes. Engaging governmental bodies and policymakers is imperative to ensure that research findings translate into actionable conservation measures. This can promote integration of conservation strategies into larger land management frameworks. By adopting a forward-thinking mindset, researchers and conservationists can enhance the chances of marsupials thriving across their habitats, ultimately preserving these unique marsupial species for future generations.
In conclusion, assessing habitat connectivity for marsupial movement is integral to ensuring their survival as urbanization and environmental pressures increase. By mapping and analyzing ecological corridors, scientists can identify critical areas that facilitate species movement, encounter challenges in habitat fragmentation, and uncover new strategies for conservation. Involving local communities, leveraging modern technology, and prioritizing adaptable research methodologies are keys to enhancing the impact of conservation efforts. Such concerted efforts not only protect marsupial populations but foster a deeper connection between people and the ecosystems they inhabit. Conservation is not merely an obligation but an opportunity to innovate and collaborate for a sustainable future. We must remain vigilant and proactive, adapting our approaches as necessary to ensure that marsupials continue to thrive across landscapes that are both diverse and dynamic. Ultimately, the future of marsupials depends on a collective commitment to preserving their habitats and ensuring connectivity remains a priority for conservation professionals, policymakers, and communities alike. By embracing these strategies and promoting awareness, we pave the way for a more resilient and biodiverse environment.
Call to Action
As we move forward, it is essential to encourage and support conservation initiatives focused on habitat connectivity for marsupial species. Everyone can contribute to this cause by educating themselves about local marsupial populations and participating in related conservation activities. Individuals can join local conservation organizations or volunteer for habitat restoration projects that enhance ecological corridors. By raising public awareness about the importance of these habitats, we can inspire action beyond our communities. Furthermore, promoting policies that emphasize habitat connectivity and legislative frameworks can provide the necessary support for ongoing research and environmental conservation. Many stakeholders must collaborate to create a robust network that facilitates marsupial movement and ensures their long-term survival. Our collective responsibility requires us to address these issues with urgency and dedication. By spotlighting the importance of habitat connectivity for marsupials, we contribute to biodiversity and ecological health. Let us unite to champion conservation that respects the needs of both wildlife and the landscapes they inhabit. In the realm of conservation, every action, no matter how small, contributes to a larger goal: a harmonious coexistence between marsupials and their ecosystems.