The Influence of Global Trade on Vulnerable Animal Populations
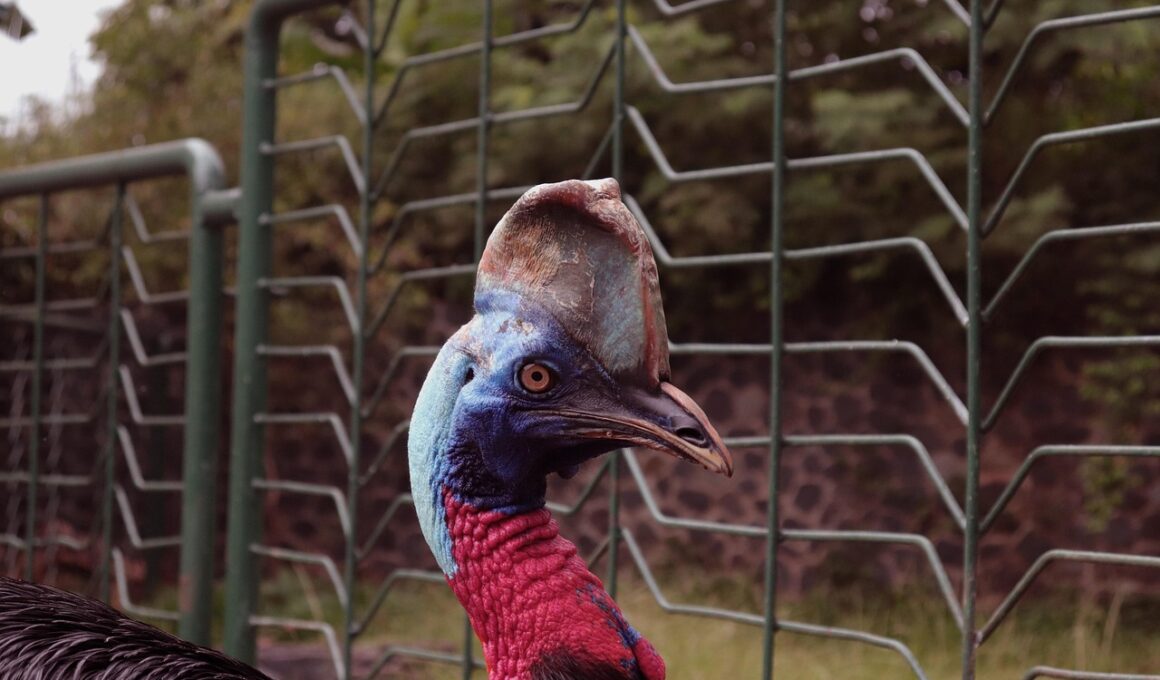
Global trade significantly impacts vulnerable animal populations worldwide, introducing various economic dynamics that often prioritize profit over ecological stability. As nations engage in commerce, demand for wildlife products surges, leading to increased poaching and habitat destruction. Regulations frequently lag behind this rapid economic activity, creating gaps that allow exploitation. For instance, species such as the Sumatran tiger and African elephant find themselves at risk due to the escalation of illegal wildlife trade. These animals are not only hunted for their ornamental value but also for medicinal ingredients based on misconceptions about their properties. International cooperation is crucial to implementing effective protections for these endangered species. Failure to adopt stricter laws can lead to irretrievable losses in biodiversity, resulting in ecological imbalance and disruption of ecosystems. The ripple effects of losing a single species can affect numerous other organisms reliant on them. It’s essential for consumers to reflect on their purchasing choices, recognizing that buying endangered species products can contribute to a broader cycle of destruction. Awareness campaigns aim to educate the public about the implications of their consumption patterns, promoting sustainable alternatives.
The Role of Legislation in Protecting Species
Effective legislation is vital in mitigating the adverse effects of global trade on vulnerable species. Local and international laws are designed to limit illicit trade practices and protect biodiversity from harmful exploitation. The CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species) serves as a cornerstone in safeguarding endangered wildlife. CITES aims to ensure that international trade does not threaten the survival of species. However, the enforcement of these laws often faces challenges, including limited resources and corruption, which impede progress. Countries must invest in robust enforcement measures while enhancing capacity for monitoring wildlife populations. Working together, they can promote sustainable development practices that benefit both communities and wildlife. Additionally, governments play an essential role in habitat conservation, establishing protected areas to provide safe havens for vulnerable species. The collaboration between conservationists, policymakers, and local communities is crucial in achieving these goals. Furthermore, public awareness initiatives can bridge the gap between legislative frameworks and community action. By fostering a sense of responsibility toward wildlife conservation, individuals can advocate for stronger policies that protect vulnerable species and their habitats effectively.
Consumer behavior significantly influences global trade practices affecting vulnerable species. More informed choices can lead to sustainable market trends, putting pressure on industries to adopt ethical guidelines. Businesses need to understand their responsibilities in wildlife preservation, ensuring that their supply chains do not contribute to species extinction. Campaigns advocating for ethical sourcing emphasize the importance of transparency within trade practices. By prioritizing environmentally friendly options, consumers can drive demand toward sustainable products designed to protect wildlife. Collaborations between all stakeholders can facilitate better practices while enhancing awareness surrounding the connection between consumerism and ecological health. Education plays a pivotal role in shaping public perception, generating understanding of endangered species’ plight and the factors driving their decline. Moreover, engaging influential figures in conservation work can amplify messages to larger audiences, thus fostering communal shifts in purchasing habits. By supporting laws that promote fair trade and conservation, local populations can help prevent overexploitation of endangered species. Sustainable tourism also offers economic opportunities for communities while promoting wildlife study and conservation. As travelers become increasingly conscious of their impact, they can contribute significantly to the protection of vulnerable ecosystems.
Vulnerable Species and Ecosystem Health
The health of ecosystems is closely tied to the presence of various vulnerable species, highlighting their critical roles in maintaining biodiversity. Species such as the snow leopard and coral reefs are not just endangered; their extinction can have dire consequences on entire ecosystems. When one species is removed from its habitat, it can lead to a domino effect, destabilizing other species and disrupting food webs. For example, the decline of top predators often results in an overflow of herbivore populations that can subsequently overgraze environments, further affecting biodiversity. Ecosystem services provided by these species, including natural pest control and pollination, are vital for human livelihoods. Protecting vulnerable species is imperative not only for preserving nature but also for sustaining the ecological functions that support human life. Therefore, successful conservation efforts must incorporate ecosystem management strategies focusing on protecting various species. Implementing multilevel conservation approaches that engage communities offers significant promise in tackling these challenges. Collaborative efforts can create solutions to balance human and wildlife needs, ensuring that both can thrive. Protecting these vulnerable species is to safeguard our planet’s future, considering that humans directly benefit from diverse ecosystems.
International cooperation is essential in combating global trade’s detrimental impact on vulnerable species. Collaborative frameworks help unify efforts across borders, ensuring that no species is neglected in conservation strategies. Joining forces allows nations to share data as well as successful practices while fostering collective action against illegal wildlife traffickers. Organizations such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and TRAFFIC play vital roles in facilitating this cooperation. These organizations raise awareness, conduct research, and implement programs designed to strengthen conservation efforts. Moreover, they connect local communities with global initiatives, empowering them to protect their native species. Collaborative investigations can expose trade routes and reveal how global markets influence local wildlife populations. Furthermore, partnerships with private sectors often provide necessary funding and tech innovations essential for wildlife conservation. By combining resources, countries can develop comprehensive strategies capable of addressing complex conservation issues posed by global trade. Policymakers must remain vigilant, as changes in trade policies can have immediate impacts on wildlife populations. Ultimately, persistent global outreach and commitment are required to create resilient frameworks that safeguard vulnerable species for future generations.
Community Involvement in Conservation Efforts
Engaging local communities in conservation initiatives significantly enhances efforts to protect vulnerable species. When communities recognize the intrinsic value of wildlife, they are more likely to participate actively in conservation practices. By involving locals in decision-making processes surrounding wildlife management, conservation initiatives can better address the unique challenges they face. This grassroots approach promotes stewardship, fostering a deep connection between people and their environment. Community-led tourism offers an alternative livelihood, paving the way for sustainable economic development while encouraging wildlife protection. For instance, programs that promote responsible wildlife viewing provide educational opportunities and empower communities to become conservation advocates. Additionally, financial incentives can be established to reward conservation efforts, such as reforestation or habitat restoration. By incentivizing the protection of vulnerable species, communities can see the tangible benefits of working toward a healthier ecosystem. Raising awareness through local events and educational programs can further strengthen this commitment. Vulnerable species require every support available to ensure their survival, thus a unified approach involving local communities can make a significant impact in conserving biodiversity and enhancing ecosystem stability.
Scientific research is paramount in understanding the implications of global trade on vulnerable species. Continued exploration and investigation into how trade affects wildlife populations can shape better conservation strategies and policies. By assessing population dynamics, reproduction rates, and habitat needs, researchers can provide valuable data that informs action plans aimed at preventing further decline. Tracking technological advancements in tracking and monitoring wildlife also improves our understanding of population movements and interactions with trade factors. Additionally, collaborating with local communities allows scientists to gather insights that inform research, enabling them to address practical concerns. The establishment of protected areas and wildlife corridors is necessary, but ongoing research is vital for assessing their effectiveness. Furthermore, engaging the public in citizen science projects can help gather vast amounts of data while fostering a sense of ownership over conservation initiatives. Education programs can empower individuals of all ages to participate actively in wildlife research and conservation efforts. Ultimately, equipping communities with scientific insights can instill a sense of responsibility and urgency to protect vulnerable species at risk from the ongoing consequences of global trade.
Promoting a culture of conservation is crucial for addressing the vulnerabilities faced by endangered species. Institutions, governments, and organizations must work together to engage and educate the public on wildlife conservation. Public service announcements, educational materials, and social media campaigns can foster a broader understanding of endangered species’ challenges, ensuring people recognize their role as custodians of the environment. Educational programs in schools can lay the groundwork for future generations to appreciate biodiversity and actively support conservation efforts. Workshops, demonstrations, and field trips can spark interest in local wildlife and ecosystems. Community engagement through events and initiatives can unite individuals, fostering a shared commitment to conservation. Additionally, partnerships with influential media outlets can amplify these messages, reaching broader audiences. Global events like World Wildlife Day can serve as platforms to raise awareness and rally support for vulnerable species. The commitment to conservation must translate to action, empowering individuals to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives. Supporting legislation aimed at protecting wildlife and participating in local conservation efforts transforms knowledge into impactful change. Ultimately, the collective effort to protect vulnerable species can drive positive, lasting environmental change in ecosystems worldwide.